Molecular basis of telaprevir resistance due to V36 and T54 mutations in the NS3-4A protease of the hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 18215275
- PMCID: PMC2395260
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-1-r16
Molecular basis of telaprevir resistance due to V36 and T54 mutations in the NS3-4A protease of the hepatitis C virus
Abstract
Background: The inhibitor telaprevir (VX-950) of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease NS3-4A has been tested in a recent phase 1b clinical trial in patients infected with HCV genotype 1. This trial revealed residue mutations that confer varying degrees of drug resistance. In particular, two protease positions with the mutations V36A/G/L/M and T54A/S were associated with low to medium levels of drug resistance during viral breakthrough, together with only an intermediate reduction of viral replication fitness. These mutations are located in the protein interior and far away from the ligand binding pocket.
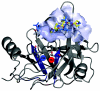
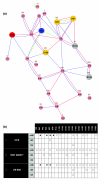
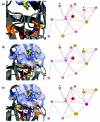
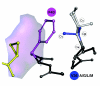
Results: Based on the available experimental structures of NS3-4A, we analyze the binding mode of different ligands. We also investigate the binding mode of VX-950 by protein-ligand docking. A network of non-covalent interactions between amino acids of the protease structure and the interacting ligands is analyzed to discover possible mechanisms of drug resistance. We describe the potential impact of V36 and T54 mutants on the side chain and backbone conformations and on the non-covalent residue interactions. We propose possible explanations for their effects on the antiviral efficacy of drugs and viral fitness. Molecular dynamics simulations of T54A/S mutants and rotamer analysis of V36A/G/L/M side chains support our interpretations. Experimental data using an HCV V36G replicon assay corroborate our findings.
Conclusion: T54 mutants are expected to interfere with the catalytic triad and with the ligand binding site of the protease. Thus, the T54 mutants are assumed to affect the viral replication efficacy to a larger degree than V36 mutants. Mutations at V36 and/or T54 result in impaired interaction of the protease residues with the VX-950 cyclopropyl group, which explains the development of viral breakthrough variants.
Figures




References
-
- Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P, Ramadori G, Bodenheimer H Jr, Bernstein D, Rizzetto M, Zeuzem S, Pockros PJ, Lin A, Ackrill AM. PEGASYS International Study Group. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:346–355. - PubMed
-
- Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958–965. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06102-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bogen SL, Arasappan A, Bennett F, Chen K, Jao E, Liu YT, Lovey RG, Venkatraman S, Pan W, Parekh T, Pike RE, Ruan S, Liu R, Baroudy B, Agrawal S, Chase R, Ingravallo P, Pichardo J, Prongay A, Brisson J-M, Hsieh TY, Cheng K-C, Kemp SJ, Levy OE, Lim-Wilby M, Tamura SY, Saksena AK, Girijavallabhan V, Njoroge FG. Discovery of SCH446211 (SCH6): a new ketoamide inhibitor of the HCV NS3 serine protease and HCV subgenomic RNA replication. J Med Chem. 2006;49:2750–2757. doi: 10.1021/jm060077j. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

