Early motor neuron pool identity and muscle nerve trajectory defined by postmitotic restrictions in Nkx6.1 activity
- PMID: 18215620
- PMCID: PMC2276619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.033
Early motor neuron pool identity and muscle nerve trajectory defined by postmitotic restrictions in Nkx6.1 activity
Abstract
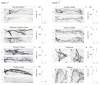
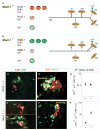
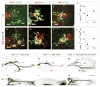
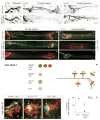
The fidelity with which spinal motor neurons innervate their limb target muscles helps to coordinate motor behavior, but the mechanisms that determine precise patterns of nerve-muscle connectivity remain obscure. We show that Nkx6 proteins, a set of Hox-regulated homeodomain transcription factors, are expressed by motor pools soon after motor neurons leave the cell cycle, before the formation of muscle nerve side branches in the limb. Using mouse genetics, we show that the status of Nkx6.1 expression in certain motor neuron pools regulates muscle nerve formation, and the pattern of innervation of individual muscles. Our findings provide genetic evidence that neurons within motor pools possess an early transcriptional identity that controls target muscle specificity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Hox regulatory network establishes motor neuron pool identity and target-muscle connectivity.Cell. 2005 Nov 4;123(3):477-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.009. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16269338
-
Specification of motor axon trajectory by ephrin-B:EphB signaling: symmetrical control of axonal patterning in the developing limb.Neuron. 2008 Dec 26;60(6):1039-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.011. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 19109910
-
A novel temporal identity window generates alternating Eve+/Nkx6+ motor neuron subtypes in a single progenitor lineage.Neural Dev. 2020 Jul 28;15(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13064-020-00146-6. Neural Dev. 2020. PMID: 32723364 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional codes and the control of neuronal identity.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002;25:251-81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142916. Epub 2002 Mar 27. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12052910 Review.
-
Transcriptional mechanisms controlling motor neuron diversity and connectivity.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008 Feb;18(1):36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.04.002. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18524570 Review.
Cited by
-
Muscle-selective RUNX3 dependence of sensorimotor circuit development.Development. 2019 Oct 24;146(20):dev181750. doi: 10.1242/dev.181750. Development. 2019. PMID: 31575648 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted roles of microRNAs: From motor neuron generation in embryos to degeneration in spinal muscular atrophy.Elife. 2019 Nov 18;8:e50848. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50848. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31738166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of functional posterior spinal motor neurons from hPSCs-derived human spinal cord neural progenitor cells.Cell Regen. 2023 Mar 23;12(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13619-023-00159-6. Cell Regen. 2023. PMID: 36949352 Free PMC article.
-
Motor neurons and the generation of spinal motor neuron diversity.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Oct 9;8:293. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00293. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25346659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct and developmentally regulated activity-dependent plasticity at descending glutamatergic synapses on flexor and extensor motoneurons.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 22;6:28522. doi: 10.1038/srep28522. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27329279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arber S, Ladle DR, Lin JH, Frank E, Jessell TM. ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons. Cell. 2000;101:485–498. - PubMed
-
- Broihier HT, Kuzin A, Zhu Y, Odenwald W, Skeath JB. Drosophila homeodomain protein Nkx6 coordinates motoneuron subtype identity and axonogenesis. Development. 2004;131:5233–5242. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter EM. Hox genes and spinal cord development. Dev Neurosci. 2002;24:24–34. - PubMed
-
- Dasen JS, Liu JP, Jessell TM. Motor neuron columnar fate imposed by sequential phases of Hox-c activity. Nature. 2003;425:926–933. - PubMed
-
- Dasen JS, Tice BC, Brenner-Morton S, Jessell TM. A Hox regulatory network establishes motor neuron pool identity and target-muscle connectivity. Cell. 2005;123:477–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

