Analysis of the substrate specificity of the Dim-5 histone lysine methyltransferase using peptide arrays
- PMID: 18215768
- PMCID: PMC2723807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.11.013
Analysis of the substrate specificity of the Dim-5 histone lysine methyltransferase using peptide arrays
Abstract
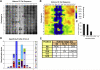
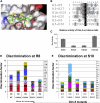
Histone methylation is an epigenetic mark essential for gene regulation and development. We introduce peptide SPOT synthesis to study sequence specificity of the Dim-5 histone-3 lysine-9 methyltransferase. Dim-5 recognizes R8-G12 of the H3 tail with T11 and G12 being the most important specificity determinants. Exchange of H3 tail residue S10 and T11 by E strongly reduced methylation by Dim-5, suggesting that phosphorylation of S10 or T11 may regulate the activity of Dim-5. In the Dim-5/peptide structure, E227 interacts with H3R8 and D209 with H3-S10. Mutations of E227 or D209 caused predictable changes in the substrate preference, illustrating that peptide recognition of histone methyltransferases can be altered by protein design. Comparative analyses of peptide arrays with wild-type and mutant enzymes, therefore, are well suited to investigate the target specificity of protein methyltransferases and study epigenetic crosstalk.
Figures

References
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–412. - PubMed
-
- Bialek K, Swistowski A, Frank R. Epitope-targeted proteome analysis: towards a large-scale automated protein-protein-interaction mapping utilizing synthetic peptide arrays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003;376:1006–1013. - PubMed
-
- Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA. Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature. 2004;429:457–463. - PubMed
-
- Feinberg AP, Tycko B. The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004;4:143–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

