Scavenger receptor class B is required for hepatitis C virus uptake and cross-presentation by human dendritic cells
- PMID: 18216094
- PMCID: PMC2268490
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02478-07
Scavenger receptor class B is required for hepatitis C virus uptake and cross-presentation by human dendritic cells
Abstract
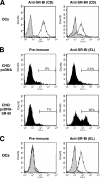
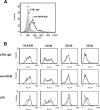
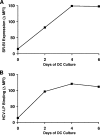
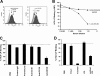
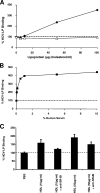
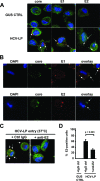
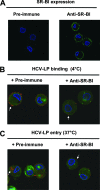
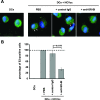
Class B scavenger receptors (SR-Bs) bind lipoproteins and play an important role in lipid metabolism. Most recently, SR-B type I (SR-BI) and its splicing variant SR-BII have been found to mediate bacterial adhesion and cytosolic bacterial invasion in mammalian cells. In this study, we demonstrate that SR-BI is a key host factor required for hepatitis C virus (HCV) uptake and cross-presentation by human dendritic cells (DCs). Whereas monocytes and T and B cells were characterized by very low or undetectable SR-BI expression levels, human DCs demonstrated a high level of cell surface expression of SR-BI similar to that of primary human hepatocytes. Antibodies targeting the extracellular loop of SR-BI efficiently inhibited HCV-like particle binding, uptake, and cross-presentation by human DCs. Moreover, human high-density lipoprotein specifically modulated HCV-like particle binding to DCs, indicating an interplay of HCV with the lipid transfer function of SR-BI in DCs. Finally, we demonstrate that anti-SR-BI antibodies inhibit the uptake of cell culture-derived HCV (HCVcc) in DCs. In conclusion, these findings identify a novel function of SR-BI for viral antigen uptake and recognition and may have an important impact on the design of HCV vaccines and immunotherapeutic approaches aiming at the induction of efficient antiviral immune responses.
Figures


References
-
- Ackerman, A. L., and P. Cresswell. 2004. Cellular mechanisms governing cross-presentation of exogenous antigens. Nat. Immunol. 5678-684. - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., R. Cerino, M. Arcuri, M. Hoffmann, P. Schurmann, M. I. Adah, B. Gissler, X. Zhao, V. Ghisetti, B. Lavezzo, H. E. Blum, F. von Weizsacker, A. Vitelli, E. Scarselli, and T. F. Baumert. 2005. Scavenger receptor class B type I and hepatitis C virus infection of primary tupaia hepatocytes. J. Virol. 795774-5785. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., T. J. Liang, and T. F. Baumert. 2006. Hepatitis C virus entry: molecular biology and clinical implications. Hepatology 44527-535. - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., C. Schafer, M. I. Adah, F. Zhang, R. J. Linhardt, H. Toyoda, A. Kinoshita-Toyoda, T. Toida, T. H. Van Kuppevelt, E. Depla, F. Von Weizsacker, H. E. Blum, and T. F. Baumert. 2003. Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 27841003-41012. - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., A. Ulsenheimer, G. R. Pape, H. M. Diepolder, M. Hoffmann, C. Neumann-Haefelin, R. Thimme, P. Henneke, R. Klein, G. Paranhos-Baccala, E. Depla, T. J. Liang, H. E. Blum, and T. F. Baumert. 2005. Uptake and presentation of hepatitis C virus-like particles by human dendritic cells. Blood 1053605-3614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

