Early phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway activation limits poliovirus-induced JNK-mediated cell death
- PMID: 18216097
- PMCID: PMC2268503
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02020-07
Early phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway activation limits poliovirus-induced JNK-mediated cell death
Abstract
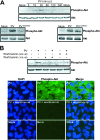
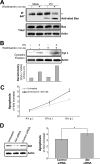
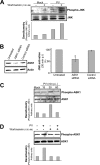
Poliovirus (PV)-induced apoptosis seems to play a major role in tissue injury in the central nervous system (CNS). We have previously shown that this process involves PV-induced Bax-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by early JNK activation in IMR5 neuroblastoma cells. We showed here that PV simultaneously activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt survival signaling pathway in these cells, limiting the extent of JNK activation and thereby cell death. JNK inhibition is associated with PI3K-dependent negative regulation of the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1, which acts upstream from JNK in PV-infected IMR5 cells. In poliomyelitis, this survival pathway may limit the spread of PV-induced damage in the CNS.
Figures

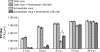
References
-
- Aikin, R., D. Maysinger, and L. Rosenberg. 2004. Cross-talk between phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT and c-jun NH2-terminal kinase mediates survival of isolated human islets. Endocrinology 1454522-4531. - PubMed
-
- Ammendolia, M. G., A. Tinari, A. Calcabrini, and F. Superti. 1999. Poliovirus infection induces apoptosis in CaCo-2 cells. J. Med. Virol. 59122-129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

