IRF-3 activation by Sendai virus infection is required for cellular apoptosis and avoidance of persistence
- PMID: 18216110
- PMCID: PMC2268502
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02536-07
IRF-3 activation by Sendai virus infection is required for cellular apoptosis and avoidance of persistence
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(14):7248
Abstract
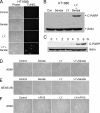
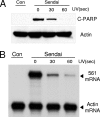
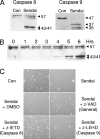
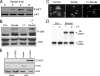
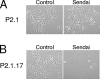
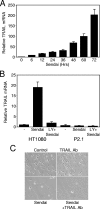
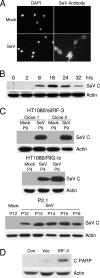
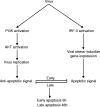
Here, we report that specific manipulations of the cellular response to virus infection can cause prevention of apoptosis and consequent establishment of persistent infection. Infection of several human cell lines with Sendai virus (SeV) or human parainfluenza virus 3, two prototypic paramyxoviruses, caused slow apoptosis, which was markedly accelerated upon blocking the action of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3 kinases) in the infected cells. The observed apoptosis required viral gene expression and the action of the caspase 8 pathway. Although virus infection activated PI3 kinase, as indicated by AKT activation, its blockage did not inhibit JNK activation or IRF-3 activation. The action of neither the Jak-STAT pathway nor the NF-kappaB pathway was required for apoptosis. In contrast, IRF-3 activation was essential, although induction of the proapototic protein TRAIL by IRF-3 was not required. When IRF-3 was absent or its activation by the RIG-I pathway was blocked, SeV established persistent infection, as documented by viral protein production and infectious virus production. Introduction of IRF-3 in the persistently infected cells restored the cells' ability to undergo apoptosis. These results demonstrated that in our model system, IRF-3 controlled the fate of the SeV-infected cells by promoting apoptosis and preventing persistence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of interferon regulatory factor 3-mediated apoptosis in the establishment and maintenance of persistent infection by Sendai virus.J Virol. 2013 Jan;87(1):16-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01853-12. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23077293 Free PMC article.
-
Paramyxovirus Sendai virus V protein counteracts innate virus clearance through IRF-3 activation, but not via interferon, in mice.Virology. 2007 Mar 1;359(1):82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.08.053. Epub 2006 Oct 6. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17027894
-
Analysis of genes induced by Sendai virus infection of mutant cell lines reveals essential roles of interferon regulatory factor 3, NF-kappaB, and interferon but not toll-like receptor 3.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):3920-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.3920-3929.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767394 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3.Cell. 2005 Sep 9;122(5):669-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.012. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16125763
-
Convergence of the NF-kappaB and interferon signaling pathways in the regulation of antiviral defense and apoptosis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Dec;1010:237-48. doi: 10.1196/annals.1299.042. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 15033728 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of interferon regulatory factor 3-mediated apoptosis in the establishment and maintenance of persistent infection by Sendai virus.J Virol. 2013 Jan;87(1):16-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01853-12. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23077293 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-viral and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the innate immune transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 3: relevance to human CNS diseases.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;8(1):132-44. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9360-5. Epub 2012 Jun 10. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22684309 Review.
-
Akt inhibitor Akt-IV blocks virus replication through an Akt-independent mechanism.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(22):11665-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01092-09. Epub 2009 Sep 9. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19740993 Free PMC article.
-
Viral apoptosis is induced by IRF-3-mediated activation of Bax.EMBO J. 2010 May 19;29(10):1762-73. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.50. Epub 2010 Apr 1. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20360684 Free PMC article.
-
Transfected poly(I:C) activates different dsRNA receptors, leading to apoptosis or immunoadjuvant response in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 27;290(9):5470-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601625. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25568326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boatright, K. M., M. Renatus, F. L. Scott, S. Sperandio, H. Shin, I. M. Pedersen, J. E. Ricci, W. A. Edris, D. P. Sutherlin, D. R. Green, and G. S. Salvesen. 2003. A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol. Cell 11529-541. - PubMed
-
- Boatright, K. M., and G. S. Salvesen. 2003. Mechanisms of caspase activation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15725-731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

