The insulin-like growth factor pathway is altered in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 and type 7
- PMID: 18216249
- PMCID: PMC2234131
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711257105
The insulin-like growth factor pathway is altered in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 and type 7
Abstract
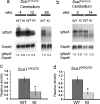
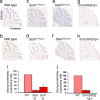
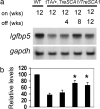
Polyglutamine diseases are inherited neurodegenerative disorders caused by expansion of CAG repeats encoding a glutamine tract in the disease-causing proteins. There are nine disorders, each having distinct features but also clinical and pathological similarities. In particular, spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 and 7 (SCA1 and SCA7) patients manifest cerebellar ataxia with degeneration of Purkinje cells. To determine whether the disorders share molecular pathogenic events, we studied two mouse models of SCA1 and SCA7 that express the glutamine-expanded protein from the respective endogenous loci. We found common transcriptional changes, with down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (Igfbp5) representing one of the most robust changes. Igfbp5 down-regulation occurred in granule neurons through a non-cell-autonomous mechanism and was concomitant with activation of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) pathway and the type I IGF receptor on Purkinje cells. These data define one common pathogenic response in SCA1 and SCA7 and reveal the importance of intercellular mechanisms in their pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Orr HT, Zoghbi HY. Trinucleotide repeat disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:575–621. - PubMed
-
- Stevanin G, et al. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7. In: Hayden MR, Rubinsztein DC, editors. Analysis of Triplet Repeat Disorders. Oxford, UK: BIOS Scientific; 1998. pp. 155–168.
-
- Serra HG, et al. RORalpha-mediated Purkinje cell development determines disease severity in adult SCA1 mice. Cell. 2006;127:697–708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

