Severe spotted fever group rickettsiosis, Australia
- PMID: 18217560
- PMCID: PMC3375793
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1311.070099
Severe spotted fever group rickettsiosis, Australia
Abstract
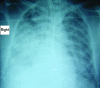
We report 3 cases of spotted fever group rickettsial infection (presumed Queensland tick typhus) in residents of northern Queensland, Australia, who had unusually severe clinical manifestations. Complications included renal failure, purpura fulminans, and severe pneumonia. Clinical illness caused by Rickettsia australis may not be as benign as previously described.
Figures
References
-
- Sexton DJ, Dwyer B, Kemp R, Graves S. Spotted fever group rickettsial infections in Australia. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:876–86. - PubMed
-
- Pinn TG, Sowden D. Queensland tick typhus. Aust N Z J Med. 1998;28:824–6. - PubMed
-
- Sexton DJ, King G, Dwyer B. Fatal Queensland tick typhus [letter]. J Infect Dis. 1990;162:779–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical