Ribonomic and short hairpin RNA gene silencing methods to explore functional gene programs associated with tumor growth arrest
- PMID: 18217689
- PMCID: PMC2517179
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-59745-335-6_15
Ribonomic and short hairpin RNA gene silencing methods to explore functional gene programs associated with tumor growth arrest
Abstract
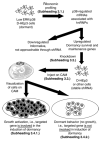
In this chapter, we present an approach using genomic and ribonomic profiling to investigate functional gene programs in a tumor growth model. To reach this goal, ribonomic profiling was combined with RNA interference in a tumor dormancy model. Strategies merging functional genomic technologies are outlined for the identification of novel posttranscriptionally regulated targets of p38 to show that they are functionally linked to the induction or interruption of cellular growth in cancer. In the first section of this chapter, we describe a method for the detection of mRNA subsets associated with RNA-binding proteins such as hnRNP A1 using (1) immunopurification of mRNA-protein complexes, from either whole cell lysates or subcellular fractions and (2) gene expression arrays to find those mRNAs bound to hnRNP A1. In the second section, short hairpin RNA technology was used to create a library of shRNAs that target p38 induced mRNAs expression libraries are utilized to "knockdown" the genes identified in the first section. Finally, this library of gene candidates is evaluated in vivo to address their functional role in the induction or maintenance of dormancy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[RNA binding proteins in the RNA interference phenomenon].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006 Jul-Aug;40(4):595-608. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006. PMID: 16913219 Review. Russian.
-
RIP-Chip analysis: RNA-Binding Protein Immunoprecipitation-Microarray (Chip) Profiling.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;703:247-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-248-9_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21125495
-
The RNA binding protein HuR differentially regulates unique subsets of mRNAs in estrogen receptor negative and estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2010 Apr 6;10:126. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-126. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20370918 Free PMC article.
-
Computational identification of a p38SAPK-regulated transcription factor network required for tumor cell quiescence.Cancer Res. 2009 Jul 15;69(14):5664-72. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3820. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19584293 Free PMC article.
-
Desperately seeking microRNA targets.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1169-74. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1921. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20924405 Review.
Cited by
-
HuR-regulated mRNAs associated with nuclear hnRNP A1-RNP complexes.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Oct 11;14(10):20256-81. doi: 10.3390/ijms141020256. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24152440 Free PMC article.
-
The In Ovo Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay as an Efficient Xenograft Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Vis Exp. 2015 Oct 9;(104):52411. doi: 10.3791/52411. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26484588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pantel K, Otte M. Occult micormetastasis: enrichment, identification and characterization of single disseminated tumor cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001;11:327–337. - PubMed
-
- Naumov GN, Townson JL, MacDonald IC, et al. Ineffectiveness of doxorubicin treatment on solitary dormant mammary carcinoma cells or late-developing metastases. Breast Cancer Treat. 2003;82:199–206. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre-Ghiso JA, Estrada Y, Liu D, Ossowski L. ERK(MAPK) activity as a determinant of tumor growth and dormancy; regulation by p38(SAPK) Cancer Res. 2003;63:1684–1695. - PubMed
-
- Clark AR, Dean JL, Saklatvala J. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression by mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:37–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

