Comparative phylogenomic analyses of teleost fish Hox gene clusters: lessons from the cichlid fish Astatotilapia burtoni: comment
- PMID: 18218066
- PMCID: PMC2246111
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-35
Comparative phylogenomic analyses of teleost fish Hox gene clusters: lessons from the cichlid fish Astatotilapia burtoni: comment
Abstract
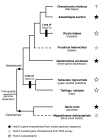
A reanalysis of the sequences reported by Hoegg et al has highlighted the presence of a putative HoxC1a gene in Astatotilapia burtoni. We discuss the evolutionary history of the HoxC1a gene in the teleost fish lineages and suggest that HoxC1a gene was lost twice independently in the Neoteleosts. This comment points out that combining several gene-finding methods and a Hox-dedicated program can improve the identification of Hox genes.
Figures

Comment on
-
Comparative phylogenomic analyses of teleost fish Hox gene clusters: lessons from the cichlid fish Astatotilapia burtoni.BMC Genomics. 2007 Sep 10;8:317. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-317. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17845724 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

