Kv1.5 association modifies Kv1.3 traffic and membrane localization
- PMID: 18218624
- PMCID: PMC2417174
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M708223200
Kv1.5 association modifies Kv1.3 traffic and membrane localization
Abstract
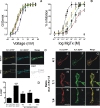
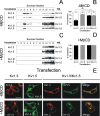
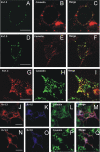
Kv1.3 activity is determined by raft association. In addition to Kv1.3, leukocytes also express Kv1.5, and both channels control physiological responses. Because the oligomeric composition may modify the channel targeting to the membrane, we investigated heterotetrameric Kv1.3/Kv1.5 channel traffic and targeting in HEK cells. Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 generate multiple heterotetramers with differential surface expression according to the subunit composition. FRET analysis and pharmacology confirm the presence of functional hybrid channels. Raft association was evaluated by cholesterol depletion, caveolae colocalization, and lateral diffusion at the cell surface. Immunoprecipitation showed that both Kv1.3 and heteromeric channels associate with caveolar raft domains. However, homomeric Kv1.3 channels showed higher association with caveolin traffic. Moreover, FRAP analysis revealed higher mobility for hybrid Kv1.3/Kv1.5 than Kv1.3 homotetramers, suggesting that heteromers target to distinct surface microdomains. Studies with lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages further supported that different physiological mechanisms govern Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 targeting to rafts. Our results implicate the traffic and localization of Kv1.3/Kv1.5 heteromers in the complex regulation of immune system cells.
Figures

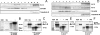

Similar articles
-
Multiple Kv1.5 targeting to membrane surface microdomains.J Cell Physiol. 2008 Dec;217(3):667-73. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21538. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18668522 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Kv1.5 and Kv1.3 contributes to the major voltage-dependent K+ channel in macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 8;281(49):37675-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605617200. Epub 2006 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17038323
-
Caveolin regulates kv1.5 trafficking to cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;73(3):678-85. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.042093. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18045854
-
Kv1.5-Kv beta interactions: molecular determinants and pharmacological consequences.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2010 Jun;10(7):635-42. doi: 10.2174/138955710791384018. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20500153 Review.
-
The secret life of ion channels: Kv1.3 potassium channels and proliferation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;314(1):C27-C42. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28931540 Review.
Cited by
-
Four and a half LIM protein 1C (FHL1C): a binding partner for voltage-gated potassium channel K(v1.5).PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026524. Epub 2011 Oct 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22053194 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of ion channels to shaping macrophage behaviour.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 7;13:970234. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.970234. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implication of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Neoplastic Cell Proliferation.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Mar 1;11(3):287. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030287. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30823672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potassium Channel Odyssey: Mechanisms of Traffic and Membrane Arrangement.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 9;20(3):734. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030734. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30744118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unconventional EGF-induced ERK1/2-mediated Kv1.3 endocytosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Apr;73(7):1515-28. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2082-0. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26542799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wulff, H., Beeton, C., and Chandy, K. G. (2003) Curr. Opin. Drug. Discov. Dev. 6 640-647 - PubMed
-
- Beeton, C., and Chandy, K. G. (2005) Neuroscientist 11 550-562 - PubMed
-
- Payet, M. D., and Dupuis, G. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267 18270-18273 - PubMed
-
- Martel, J., Dupuis, G., Deschenes, P., and Payet, M. D. (1998) J. Membr. Biol. 161 183-196 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

