Induction of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in the mediobasal hypothalamus by bacterial lipopolysaccharide: role of corticosterone
- PMID: 18218695
- PMCID: PMC2329263
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1697
Induction of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in the mediobasal hypothalamus by bacterial lipopolysaccharide: role of corticosterone
Abstract
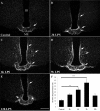
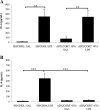
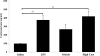
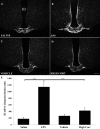
To determine whether endotoxin-induced activation of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase (D2) in the mediobasal hypothalamus is dependent on circulating levels of corticosterone, the effect of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on D2 gene expression was studied in adrenalectomized, corticosterone-clamped adult, male, Sprague Dawley rats. In sham-adrenalectomized animals, LPS (250 microg/100 g body weight) increased circulating levels of corticosterone and IL-6, as well as tanycyte D2 mRNA in the mediobasal hypothalamus. Adrenalectomized, corticosterone-clamped animals showed no significant rise in corticosterone after LPS, compared with saline-treated controls but increased IL-6 levels and tanycyte D2 mRNA similar to LPS-treated sham controls. To further clarify the potential role of corticosterone in the regulation of D2 gene expression by LPS, animals were administered high doses of corticosterone to attain levels similar to that observed in the LPS-treated group. No significant increase in D2 mRNA was observed in the mediobasal hypothalamus with the exception of a small subpopulation of cells in the lateral walls of the third ventricle. These data indicate that the LPS-induced increase in D2 mRNA in the mediobasal hypothalamus is largely independent of circulating corticosterone and indicate that mechanisms other than adrenal activation are involved in the regulation of most tanycyte D2-expressing cells by endotoxin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contribution of TNF-alpha and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling to type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase activation in the mediobasal hypothalamus after lipopolysaccharide administration.Endocrinology. 2010 Aug;151(8):3827-35. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0279. Epub 2010 May 25. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20501675 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide induces type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in the mediobasal hypothalamus: implications for the nonthyroidal illness syndrome.Endocrinology. 2004 Apr;145(4):1649-55. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1439. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 14684601
-
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase (D2) activation in the mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH) is independent of the LPS-induced fall in serum thyroid hormone levels.Brain Res. 2005 Sep 14;1056(1):97-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.07.021. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16095572
-
NFκB signaling is essential for the lipopolysaccharide-induced increase of type 2 deiodinase in tanycytes.Endocrinology. 2014 May;155(5):2000-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-2018. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24635351
-
Exposure to acute stress induces brain interleukin-1beta protein in the rat.J Neurosci. 1998 Mar 15;18(6):2239-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-06-02239.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9482808 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Association of non-thyroidal illness syndrome with interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in critically ill children with sepsis].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Nov;22(11):1215-1220. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2004137. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33172558 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prognostic significance of nonthyroidal illness syndrome in critically ill adult patients with sepsis.Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2018 Jul-Sep;8(3):165-172. doi: 10.4103/IJCIIS.IJCIIS_29_17. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2018. PMID: 30181975 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of TNF-alpha and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling to type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase activation in the mediobasal hypothalamus after lipopolysaccharide administration.Endocrinology. 2010 Aug;151(8):3827-35. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0279. Epub 2010 May 25. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20501675 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid hormone and the neuroglia: both source and target.J Thyroid Res. 2011;2011:215718. doi: 10.4061/2011/215718. Epub 2011 Aug 23. J Thyroid Res. 2011. PMID: 21876836 Free PMC article.
-
Tanycyte pyroglutamyl peptidase II contributes to regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis through glial-axonal associations in the median eminence.Endocrinology. 2009 May;150(5):2283-91. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1643. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19179432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR 2002 Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology, and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocr Rev 23:38–89 - PubMed
-
- Kohrle J 2000 The selenoenzyme family of deiodinase isozymes controls local thyroid hormone availability. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 1:49–58 - PubMed
-
- Lechan RM, Fekete C 2005 Role of thyroid hormone deiodination in the hypothalamus. Thyroid 15:883–897 - PubMed
-
- Tu HM, Kim SW, Salvatore D, Bartha T, Legradi G, Larsen PR, Lechan RM 1997 Regional distribution of type 2 thyroxine deiodinase messenger ribonucleic acid in rat hypothalamus and pituitary and its regulation by thyroid hormone. Endocrinology 138:3359–3368 - PubMed

