Nuclear hormone receptors for heme: REV-ERBalpha and REV-ERBbeta are ligand-regulated components of the mammalian clock
- PMID: 18218725
- PMCID: PMC5419435
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2007-0519
Nuclear hormone receptors for heme: REV-ERBalpha and REV-ERBbeta are ligand-regulated components of the mammalian clock
Abstract
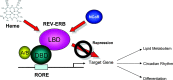
The nuclear hormone receptors (NHRs), REV-ERBalpha and REV-ERBbeta, regulate a number of physiological functions including the circadian rhythm, lipid metabolism, and cellular differentiation. These two receptors lack the activation function-2 region that is associated with the ability of NHRs to recruit coactivators and activate target gene transcription. These NHRs have been characterized as constitutive repressors of transcription due to their lack of an identified ligand and their strong ability to recruit the corepressor, nuclear receptor corepressor. Recently, the porphyrin heme was demonstrated to function as a ligand for both REV-ERBs. Heme binds directly to the ligand-binding domain and regulates the ability of these NHRs to recruit nuclear receptor corepressor to target gene promoters. This review focuses on the physiological roles that these two receptors play and the implications of heme functioning as their ligand. The prospect that these NHRs, now known to be regulated by small molecule ligands, may be targets for development of drugs for treatment of diseases associated with aberrant circadian rhythms including metabolic and psychiatric disorders as well as cancer is also addressed.
Figures
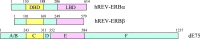

References
-
- Savkur RS, Bramlett KS, Clawson D, Burris TP 2004. Pharmacology of nuclear receptor-coregulator recognition. In: Vitamins and hormones. Vol 68. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press; 145–183 - PubMed
-
- Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM 1995. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 83:841–850 - PubMed
-
- Savkur RS, Burris TP 2004. The coactivator LXXLL nuclear receptor recognition motif. J Peptide Res 63:207–212 - PubMed
-
- Lonard DM, O'Malley BW 2007. Nuclear receptor coregulators: judges, juries, and executioners of cellular regulation. Mol Cell 27:691–700 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

