C-Jun NH2 terminal kinase (JNK) is an essential mediator of Toll-like receptor 2-induced corneal inflammation
- PMID: 18218857
- PMCID: PMC3959745
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.1107783
C-Jun NH2 terminal kinase (JNK) is an essential mediator of Toll-like receptor 2-induced corneal inflammation
Abstract
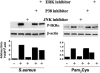
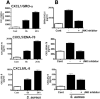
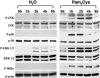
TLRs play an important role in the host inflammatory response to bacteria and bacterial products by activating a cascade of intracellular events leading to production of proinflammatory and chemotactic cytokines. To determine the role of MAPKs in TLR- induced corneal inflammation, we stimulated human corneal epithelial (HCE) cells with TLR2 ligands, tripalmitoyl-S-glycero-Cys-(Lys)4 (Pam3Cys) or inactivated Staphylococcus aureus, and examined the time course of expression of MAPKs and the effect of MAPK inhibition on IkBalpha degradation and CXC chemokine production. We found that S. aureus and Pam3Cys stimulate phosphorylation of JNK, p38 MAPK, and ERK within 4 h and that blockade of JNK, but not p38 or ERK phosphorylation, had an inhibitory effect on IkBalpha degradation and CXC chemokine production. To determine if JNK is also important in TLR2-induced corneal inflammation in vivo, we examined JNK1(-/-) mice and pharmacological inhibitors in a murine model of TLR2-induced corneal inflammation which is characterized by neutrophil recruitment to the corneal stroma and development of corneal haze. We found that corneal inflammation was significantly impaired in JNK1(-/-) mice compared with control mice, and in mice treated with the JNK inhibitor compared with vehicle control. Taken together with results from HCE cells, these findings demonstrate that JNK has an essential role in TLR2-induced corneal inflammation.
Figures

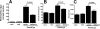
Similar articles
-
Staphylococcus aureus-induced corneal inflammation is dependent on Toll-like receptor 2 and myeloid differentiation factor 88.Infect Immun. 2006 Sep;74(9):5325-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00645-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16926427 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of toll-like receptor (TLR)2, TLR4, and TLR9 in the mammalian cornea induces MyD88-dependent corneal inflammation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Feb;46(2):589-95. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-1077. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15671286
-
Gamma interferon and interleukin-1 receptor 1 regulate neutrophil recruitment to the corneal stroma in a murine model of Onchocerca volvulus keratitis.Infect Immun. 2009 Apr;77(4):1606-12. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00671-08. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19168746 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 2 regulates CXC chemokine production and neutrophil recruitment to the cornea in Onchocerca volvulus/Wolbachia-induced keratitis.Infect Immun. 2007 Dec;75(12):5908-15. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00991-07. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17875630 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal Involvement in HIV-infected Individuals.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2021 Aug 18;29(6):1177-1182. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2021.1887283. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34232799 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Streptococcus pneumoniae Keratitis and STAT3-Dependent Expression of LL-37 by Streptococcus pneumoniae in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells.Pathogens. 2019 Mar 6;8(1):31. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8010031. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 30845777 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-metabolite network analysis in different nonalcoholic fatty liver disease phenotypes.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Jan 13;49(1):e283. doi: 10.1038/emm.2016.123. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28082742 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-life role for c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase at rostral ventrolateral medulla in experimental brain stem death.J Biomed Sci. 2012 Nov 17;19(1):96. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-96. J Biomed Sci. 2012. PMID: 23157661 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Black Ginseng Water Extract under the Inflammatory Conditions of Cultured Sebocytes and Outer Root Sheath Cells.Ann Dermatol. 2022 Apr;34(2):95-104. doi: 10.5021/ad.2022.34.2.95. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Ann Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35450316 Free PMC article.
-
Osmoprotective effects of supplemental epidermal growth factor in an ex vivo multilayered human conjunctival model under hyperosmotic stress.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013 Aug;251(8):1945-53. doi: 10.1007/s00417-013-2369-5. Epub 2013 May 16. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23677487
References
-
- Hume EB, Dajcs JJ, Moreau JM, Sloop GD, Willcox MD, O'Callaghan RJ. Staphylococcus corneal virulence in a new topical model of infection. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001;42:2904–2908. - PubMed
-
- Girgis DO, Sloop GD, Reed JM, O'Callaghan RJ. A new topical model of Staphylococcus corneal infection in the mouse. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003;44:1591–1597. - PubMed
-
- Hume EB, Cole N, Khan S, Garthwaite LL, Aliwarga Y, Schubert TL, Willcox MD. A Staphylococcus aureus mouse keratitis topical infection model: cytokine balance in different strains of mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2005;83:294–300. - PubMed
-
- Sloop GD, Moreau JM, Conerly LL, Dajcs JJ, O'Callaghan RJ. Acute inflammation of the eyelid and cornea in Staphylococcus keratitis in the rabbit. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999;40:385–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

