Neurovascular responses to mental stress in the supine and upright postures
- PMID: 18218909
- PMCID: PMC3608133
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01285.2007
Neurovascular responses to mental stress in the supine and upright postures
Abstract
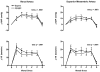
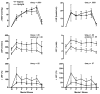
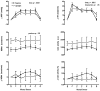
The purpose of this study was to determine neurovascular responses to mental stress (MS) in the supine and upright postures. MS was elicited in 23 subjects (26 +/- 1 yr) by 5 min of mental arithmetic. In study 1 (n = 9), Doppler ultrasound was used to measure mean blood flow velocity in the renal (RBFV) and superior mesenteric arteries (SMBFV), and venous occlusion plethysmography was used to measure forearm blood flow (FBF). In study 2 (n = 14), leg blood flow (LBF; n = 9) was measured by Doppler ultrasound, and muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA; n = 5) was measured by microneurography. At rest, upright posture increased heart rate and MSNA and decreased LBF, FBF, RBFV, and SMBFV and their respective conductances. MS elicited similar increases in mean arterial blood pressure ( approximately 12 mmHg) and heart rate ( approximately 17 beats/min), regardless of posture. MS in both postures elicited a decrease in RBFV, SMBFV, and their conductances and an increase in LBF, FBF, and their conductances. Changes in blood flow were blunted in the upright posture in all vascular beds examined, but the pattern of the vascular response was the same as the supine posture. MS did not change MSNA in either posture (change: approximately 1 +/- 3 and approximately 3 +/- 3 bursts/min, respectively). In conclusion, the augmented sympathetic activity of the upright posture does not alter heart rate, mean arterial blood pressure, or MSNA responses to MS. MS elicits divergent vascular responses in the visceral and peripheral vasculature. These results indicate that, although the upright posture attenuates vascular responses to MS, the pattern of neurovascular responses does not differ between postures.
Figures

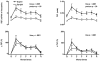
Similar articles
-
Sex differences in sympathetic neural and limb vascular reactivity to mental stress in humans.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Feb 1;304(3):H436-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00688.2012. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23203970
-
Neurovascular responses to mental stress.J Physiol. 2005 Apr 1;564(Pt 1):321-7. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.079665. Epub 2005 Feb 10. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15705649 Free PMC article.
-
Upright posture reduces forearm blood flow early in exercise.Am J Physiol. 1999 May;276(5):R1434-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1999.276.5.R1434. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10233037
-
Ecological nuances in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI): psychological stressors, posture, and hydrostatics.Neuroimage. 2005 Mar;25(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.11.015. Epub 2005 Jan 27. Neuroimage. 2005. PMID: 15734338 Review.
-
Position- and posture-dependent vascular imaging-a scoping review.Eur Radiol. 2024 Apr;34(4):2334-2351. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10154-9. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37672051 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neurovascular responses to mental stress in prehypertensive humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011 Jan;110(1):76-82. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00912.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 4. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011. PMID: 21051574 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a mental task on splanchnic blood flow in fasting and postprandial conditions.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Apr;108(6):1107-13. doi: 10.1007/s00421-009-1316-y. Epub 2009 Dec 19. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20024578
-
Sympathetic neural responses to mental stress: responders, nonresponders and sex differences.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Mar;296(3):H847-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01234.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19168718 Free PMC article.
-
Acute mental stress-caused arterial stiffening can be counteracted by brief aerobic exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021 May;121(5):1359-1366. doi: 10.1007/s00421-021-04618-3. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33604696
-
Sympathoneural and adrenomedullary responses to mental stress.Compr Physiol. 2015 Jan;5(1):119-46. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c140030. Compr Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25589266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson EA, Sinkey CA, Mark AL. Mental stress increases sympathetic nerve activity during sustained baroreceptor stimulation in humans. Hypertension. 1991;17:III43–49. - PubMed
-
- Anderson EA, Wallin BG, Mark AL. Dissociation of sympathetic nerve activity in arm and leg muscle during mental stress. Hypertension. 1987;9:III114–119. - PubMed
-
- Brod J, Fencl V, Hejl Z, Jirka J. Circulatory changes underlying blood pressure elevation during acute emotional stress (mental arithmetic) in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Clin Sci. 1959;18:269–279. - PubMed
-
- Cardillo C, Kilcoyne CM, Quyyumi AA, Cannon RO, 3rd, Panza JA. Role of nitric oxide in the vasodilator response to mental stress in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol. 1997;80:1070–1074. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

