Genome-wide expression profiling Arabidopsis at the stage of Golovinomyces cichoracearum haustorium formation
- PMID: 18218973
- PMCID: PMC2259087
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.111286
Genome-wide expression profiling Arabidopsis at the stage of Golovinomyces cichoracearum haustorium formation
Abstract
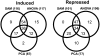
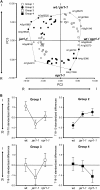
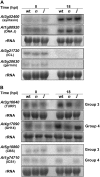
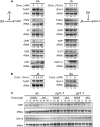
Compatibility between plants and obligate biotrophic fungi requires fungal mechanisms for efficiently obtaining nutrients and counteracting plant defenses under conditions that are expected to induce changes in the host transcriptome. A key step in the proliferation of biotrophic fungi is haustorium differentiation. Here we analyzed global gene expression patterns in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves during the formation of haustoria by Golovinomyces cichoracearum. At this time, the endogenous levels of salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) were found to be enhanced. The responses of wild-type, npr1-1, and jar1-1 plants were used to categorize the sensitivity of gene expression changes to NPR1 and JAR1, which are components of the SA and JA signaling pathways, respectively. We found that the infection process was the major source of variation, with 70 genes identified as having similarly altered expression patterns regardless of plant genotype. In addition, principal component analysis (PCA) identified genes responding both to infection and to lack of functional JAR1 (17 genes) or NPR1 (18 genes), indicating that the JA and SA signaling pathways function as secondary sources of variation. Participation of these genes in the SA or JA pathways had not been described previously. We found that some of these genes may be sensitive to the balance between the SA and JA pathways, representing novel markers for the elucidation of cross-talk points between these signaling cascades. Conserved putative regulatory motifs were found in the promoter regions of each subset of genes. Collectively, our results indicate that gene expression changes in response to infection by obligate biotrophic fungi may support fungal nutrition by promoting alterations in host metabolism. In addition, these studies provide novel markers for the characterization of defense pathways and susceptibility features under this infection condition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethylene and jasmonic acid signaling affect the NPR1-independent expression of defense genes without impacting resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and Peronospora parasitica in the Arabidopsis ssi1 mutant.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003 Jul;16(7):588-99. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.7.588. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003. PMID: 12848424
-
Enhanced defense responses in Arabidopsis induced by the cell wall protein fractions from Pythium oligandrum require SGT1, RAR1, NPR1 and JAR1.Plant Cell Physiol. 2009 May;50(5):924-34. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcp044. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19304739
-
Involvement of salicylate and jasmonate signaling pathways in Arabidopsis interaction with Fusarium graminearum.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2010 Jul;23(7):861-70. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-23-7-0861. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2010. PMID: 20521949 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives on plant defense responses through modulation of developmental pathways.Mol Cells. 2008 Aug 31;26(2):107-12. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Mol Cells. 2008. PMID: 18562800 Review.
-
The haustorium: The root of biotrophic fungal pathogens.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 29;13:963705. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.963705. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36105706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for Wheat Stripe Rust Pathogenicity Identified by Transcriptome Sequencing.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 26;8(6):e67150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067150. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840606 Free PMC article.
-
Translationally controlled tumour protein (TCTP) from tomato and Nicotiana benthamiana is necessary for successful infection by a potyvirus.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Jun;18(5):672-683. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12426. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27159273 Free PMC article.
-
The Powdery Mildew Disease of Arabidopsis: A Paradigm for the Interaction between Plants and Biotrophic Fungi.Arabidopsis Book. 2008;6:e0115. doi: 10.1199/tab.0115. Epub 2008 Oct 2. Arabidopsis Book. 2008. PMID: 22303240 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Arabidopsis translationally controlled tumor protein gene AtTCTP enhances drought tolerance with rapid ABA-induced stomatal closure.Mol Cells. 2012 Jun;33(6):617-26. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-0080-8. Epub 2012 May 17. Mol Cells. 2012. PMID: 22610367 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of rice CBS domain containing protein improves salinity, oxidative, and heavy metal tolerance in transgenic tobacco.Mol Biotechnol. 2012 Nov;52(3):205-16. doi: 10.1007/s12033-011-9487-2. Mol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22302312
References
-
- Adam L, Ellwood S, Wilson I, Saenz G, Xiao S, Oliver RP, Turner JG, Somerville S (1999) Comparison of Erysiphe cichoracearum and E. cruciferarum and a survey of 360 Arabidopsis thaliana accessions for resistance to these two powdery mildew pathogens. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12 1031–1043 - PubMed
-
- Adam L, Somerville SC (1996) Genetic characterization of five powdery mildew disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 9 341–356 - PubMed
-
- Agrawal GK, Jwa NS, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2003) Importance of ascorbate peroxidases OsAPX1 and OsAPX2 in the rice pathogen response pathways and growth and reproduction revealed by their transcriptional profiling. Gene 322 93–103 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez ME, Pennell RI, Meijer PJ, Ishikawa A, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell 92 773–784 - PubMed
-
- Bostock RM (2005) Signal cross-talk and induced resistance: straddling the line between cost and benefit. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43 545–580 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

