Early incorporation of obscurin into nascent sarcomeres: implication for myofibril assembly during cardiac myogenesis
- PMID: 18219491
- PMCID: PMC2761667
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-008-0378-y
Early incorporation of obscurin into nascent sarcomeres: implication for myofibril assembly during cardiac myogenesis
Abstract
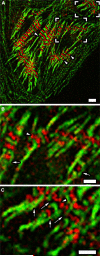
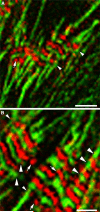
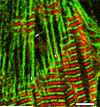
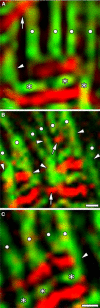
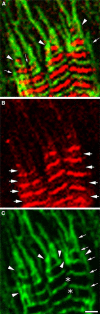
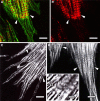
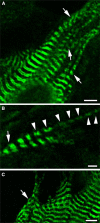
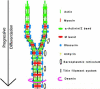
Obscurin is a recently identified giant multidomain muscle protein whose functions remain poorly understood. The goal of this study was to investigate the process of assembly of obscurin into nascent sarcomeres during the transition from non-striated myofibril precursors to striated structure of differentiating myofibrils in cell cultures of neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Double immunofluorescent labeling and high resolution confocal microscopy demonstrated intense incorporation of obscurin in the areas of transition from non-striated to striated regions on the tips of developing myofibrils and at the sites of lateral fusion of nascent sarcomere bundles. We found that obscurin rapidly and precisely accumulated in the middle of the A-band regions of the terminal newly assembled half-sarcomeres in the zones of transition from the continuous, non-striated pattern of sarcomeric alpha-actinin distribution to cross-striated structure of laterally expanding nascent Z-discs. The striated pattern of obscurin typically ended at these points. This occurred before the assembly of morphologically differentiated terminal Z-discs of the assembling sarcomeres on the tips of growing myofibrils. The presence of obscurin in the areas of the terminal Z-discs of each new sarcomere was detected at the same time or shortly after complete assembly of sarcomeric structure. Many non-striated fibers with very low concentration of obscurin were already immunopositive for sarcomeric actin and myosin. This suggests that obscurin may serve for organization and alignment of myofilaments into the striated pattern. The comparison of obscurin and titin localization in these areas showed that obscurin assembly into the A-bands occurred soon after or concomitantly with incorporation of titin. Electron microscopy of growing myofibrils demonstrated intense formation and integration of myosin filaments into the "open" half-assembled sarcomeres in the areas of the terminal Z-I structures and at the lateral surfaces of newly formed, terminally located nascent sarcomeres. This process progressed before the assembly of the second-formed, terminal Z-discs of new sarcomeres and before the development of ultrastructurally detectable mature M-lines that define the completion of myofibril assembly, which supports the data of immunocytochemical study. Abundant non-aligned sarcomeres in immature myofibrils located on the growing tips were spatially separated and underwent the transition to the registered, aligned pattern. The sarcoplasmic reticulum, the organelle known to interact with obscurin, assembled around each new sarcomere. These results suggest that obscurin is directly involved in the proper positioning and alignment of myofilaments within nascent sarcomeres and in the establishment of the registered pattern of newly assembled myofibrils and the sarcoplasmic reticulum at advanced stages of myofibrillogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Agarkova I, Perriard J-C. The M-band: an elastic web that cross-links thick filaments in the center of the sarcomere. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:477–485. - PubMed
-
- Agarkova I, Ehler E, Lange S, Schoenauer R, Perriard JC. M-band: a safeguard for sarcomeric stability? J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003;24:191–203. - PubMed
-
- Anversa P, Olivetti G, Bracchi PG, Loud AV. Postnatal development of the M-band in rat cardiac myofibrils. Circ Res. 1981;48:561–568. - PubMed
-
- Armani A, Galli S, Giacomello E, Bagnato P, Barone V, Rossi D, Sorrentino V. Molecular interactions with obscurin are involved in the localization of muscle-specific small ankyrin 1 isoforms to subcompartments of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:3456–3458. - PubMed
-
- Arimura T, Matsumoto Y, Okazaki O, Hayashi T, Takahashi M, Inagaki N, Hinohara K, Ashizawa N, Yano K, Kimura A. Structural analysis of obscurin gene in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;362:281–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

