Self-organized criticality and the development of EEG phase reset
- PMID: 18219618
- PMCID: PMC6871258
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20524
Self-organized criticality and the development of EEG phase reset
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to explore human development of self-organized criticality as measured by EEG phase reset from infancy to 16 years of age.
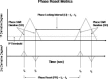
Methods: The electroencephalogram (EEG) was recorded from 19 scalp locations from 458 subjects ranging in age from 2 months to 16.67 years. Complex demodulation was used to compute instantaneous phase differences between pairs of electrodes and the 1st and 2nd derivatives were used to detect the sudden onset and offset times of a phase shift followed by an extended period of phase locking. Mean phase shift duration and phase locking intervals were computed for two symmetrical electrode arrays in the posterior-to-anterior locations and the anterior-to-posterior directions in the alpha frequency band (8-13 Hz).
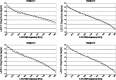
Results: Log-log spectral plots demonstrated 1/f (alpha) distributions (alpha approximately 1) with longer slopes during periods of phase shifting than during periods of phase locking. The mean duration of phase locking (150-450 msec) and phase shift (45-67 msec) generally increased as a function of age. The mean duration of phase shift declined over age in the local frontal regions but increased in distant electrode pairs. Oscillations and growth spurts from mean age 0.4-16 years were consistently present.
Conclusions: The development of increased phase stability in local systems is paralleled by lengthened periods of unstable phase in distant connections. Development of the number and/or density of synaptic connections is a likely order parameter to explain oscillations and growth spurts in self-organized criticality during human brain maturation.
Figures









References
-
- Allport DA ( 1968): Phenomenal simultaneity and perceptual moment hypotheses. Br J Psychol 59: 395–406. - PubMed
-
- Bak P ( 1996): How Nature Works: The Science of Self‐Organized Criticality. New York: Springer‐Verlag.
-
- Bak P,Tang C,Wisenfeld K ( 1987): Self‐organized criticality: An explanation of 1/f noise. Phys Rev Lett 59: 381–384. - PubMed
-
- Bak P,Tang C,Wisenfeld K ( 1988): Self‐organized criticality. Phys Rev A 38: 364–374. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

