Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells are involved in the generation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in Peyer's patches in an orally tolerized, collagen-induced arthritis mouse model
- PMID: 18221522
- PMCID: PMC2374459
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2361
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells are involved in the generation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in Peyer's patches in an orally tolerized, collagen-induced arthritis mouse model
Abstract
Introduction: The present study was devised to understand the role of systemic indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in the tolerance induction for orally tolerized mice in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). We examined whether IDO-expressing dendritic cells (DCs) are involved in the generation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells during the induction of oral tolerance in a murine CIA model.
Methods: Type II collagen was fed six times to DBA/1 mice beginning 2 weeks before immunization, and the effect on arthritis was assessed. To examine the IDO expression, the DCs of messenger RNA and protein were analyzed by RT-PCR and Flow cytometry. In addition, a proliferative response assay was also carried out to determine the suppressive effects of DCs through IDO. The ability of DCs expressing IDO to induce CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells was examined.
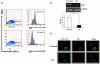
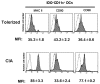
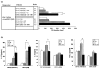
Results: CD11c+ DCs in Peyer's patches from orally tolerized mice expressed a higher level of IDO than DCs from nontolerized CIA mice. IDO-expressing CD11c+ DCs were involved in the suppression of type II collagen-specific T-cell proliferation and in the downregulation of proinflammatory T helper 1 cytokine production. The suppressive effect of IDO-expressing CD11c+ DCs was mediated by Foxp3+CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that tolerogenic CD11c+ DCs are closely linked with the induction of oral tolerance through an IDO-dependent mechanism and that this pathway may provide a new therapeutic modality to treat autoimmune arthritis.
Figures


Comment in
-
Mechanisms of oral tolerance revisited.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(2):108. doi: 10.1186/ar2402. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18466643 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Antigen-induced, tolerogenic CD11c+,CD11b+ dendritic cells are abundant in Peyer's patches during the induction of oral tolerance to type II collagen and suppress experimental collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Mar;54(3):887-98. doi: 10.1002/art.21647. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16508971
-
A distinct tolerogenic subset of splenic IDO(+)CD11b(+) dendritic cells from orally tolerized mice is responsible for induction of systemic immune tolerance and suppression of collagen-induced arthritis.Cell Immunol. 2012 Jul-Aug;278(1-2):45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Cell Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23121975
-
Dendritic cells modulated by innate immunity improve collagen-induced arthritis and induce regulatory T cells in vivo.Immunology. 2009 Jan;126(1):35-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02875.x. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 18754812 Free PMC article.
-
Type II collagen oral tolerance; mechanism and role in collagen-induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19(6):581-9. doi: 10.1007/s10165-009-0210-0. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Mod Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19697097 Review.
-
Using an ancient tool for igniting and propagating immune tolerance: IDO as an inducer and amplifier of regulatory T cell functions.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(15):2215-21. doi: 10.2174/092986711795656027. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21517758 Review.
Cited by
-
Tolerogenic splenic IDO (+) dendritic cells from the mice treated with induced-Treg cells suppress collagen-induced arthritis.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:831054. doi: 10.1155/2014/831054. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 25405209 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D: implications for GVHD.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010 Sep;45(9):1463-8. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2009.366. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010. PMID: 20081878 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 regulatory T cells specific for collagen type II as an efficient cell-based therapy in arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 May 22;16(3):R115. doi: 10.1186/ar4567. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24886976 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered erythrocytes covalently linked to antigenic peptides can protect against autoimmune disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 21;114(12):3157-3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701746114. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28270614 Free PMC article.
-
Gain‑of‑function of IDO in DCs inhibits T cell immunity by metabolically regulating surface molecules and cytokines.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Apr 3;25(5):234. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11933. eCollection 2023 May. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37114180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song F, Guan Z, Gienapp IE, Shawler T, Benson J, Whitacre CC. The thymus plays a role in oral tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2006;177:1500–1509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

