Roles of ubiquitination at the synapse
- PMID: 18222124
- PMCID: PMC2668815
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.12.010
Roles of ubiquitination at the synapse
Abstract
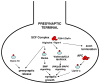
The ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) was first described as a mechanism for protein degradation more than three decades ago, but the critical roles of the UPS in regulating neuronal synapses have only recently begun to be revealed. Targeted ubiquitination of synaptic proteins affects multiple facets of the synapse throughout its life cycle; from synaptogenesis and synapse elimination to activity-dependent synaptic plasticity and remodeling. The recent identification of specific UPS molecular pathways that act locally at the synapse illustrates the exquisite specificity of ubiquitination in regulating synaptic protein trafficking and degradation events. Synaptic activity has also been shown to determine the subcellular distribution and composition of the proteasome, providing additional mechanisms for locally regulating synaptic protein degradation. Together these advances reveal that tight control of protein turnover plays a conserved, central role in establishing and modulating synapses in neural circuits.
Figures


References
-
- Jiang YH, Beaudet AL. Human disorders of ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004;16:419–426. - PubMed
-
- Reinstein E, Clechanover A. Protein degradation and human diseases: the ubiquitin connection. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145:676–684. - PubMed
-
- Ciechanover A, Brundin P. The ubiquitin proteasome system in neurodegenerative diseases: sometimes the chicken, sometimes the egg. Neuron. 2003;40:427–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

