Biophysical study of thermal denaturation of apo-calmodulin: dynamics of native and unfolded states
- PMID: 18223007
- PMCID: PMC2586555
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.120147
Biophysical study of thermal denaturation of apo-calmodulin: dynamics of native and unfolded states
Abstract
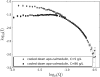
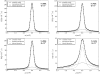
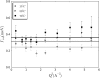
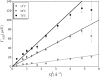
Apo-calmodulin, a small, mainly alpha, soluble protein is a calcium-dependent protein activator. This article presents a study of internal dynamics of native and thermal unfolded apo-calmodulin, using quasi-elastic neutron scattering. This technique can probe protein internal dynamics in the picosecond timescale and in the nanometer length-scale. It appears that a dynamical transition is associated with thermal denaturation of apo-calmodulin. This dynamical transition goes together with a decrease of the confinement of hydrogen atoms, a decrease of immobile protons proportion and an increase of dynamical heterogeneity. The comparison of native and unfolded states dynamics suggests that the dynamics of protein atoms is more influenced by their distance to the backbone than by their solvent exposure.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Use of SANS and biophysical techniques to reveal subtle conformational differences between native apo-calmodulin and its unfolded states.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Oct;1824(10):1097-106. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.06.001. Epub 2012 Jun 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22709575
-
High-pressure SANS and fluorescence unfolding study of calmodulin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1844(9):1560-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24862246
-
Picosecond internal dynamics of lysozyme as affected by thermal unfolding in nonaqueous environment.Biophys J. 2004 Jan;86(1 Pt 1):480-7. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74126-0. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 14695292 Free PMC article.
-
Energy landscape views for interplays among folding, binding, and allostery of calmodulin domains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 22;111(29):10550-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402768111. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25002491 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, dynamics and interaction with kinase targets: computer simulations of calmodulin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):289-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.032. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023369 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamical Behavior of Disordered Regions in Disease-Related Proteins Revealed by Quasielastic Neutron Scattering.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jun 13;58(6):795. doi: 10.3390/medicina58060795. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35744058 Free PMC article.
-
Hemoglobin dynamics in red blood cells: correlation to body temperature.Biophys J. 2008 Dec;95(11):5449-61. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.138040. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18708462 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of thermodynamically stable, kinetically trapped, and inhibitor-bound states of pepsin.Biophys J. 2011 Oct 5;101(7):1699-709. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.08.002. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21961596 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamical Behavior of Human α-Synuclein Studied by Quasielastic Neutron Scattering.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 20;11(4):e0151447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151447. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27097022 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Dimerization via Tyr Residues: Highlight of a Slow Process with Co-Existence of Numerous Intermediates and Final Products.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 21;23(3):1174. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031174. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163094 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

