Novel bacterial artificial chromosome vector pUvBBAC for use in studies of the functional genomics of Listeria spp
- PMID: 18223114
- PMCID: PMC2268298
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00415-07
Novel bacterial artificial chromosome vector pUvBBAC for use in studies of the functional genomics of Listeria spp
Abstract
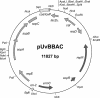
Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) vectors are important tools for microbial genome research. We constructed a novel BAC vector, pUvBBAC, for replication in both gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial hosts. The pUvBBAC vector was used to generate a BAC library for the facultative intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e. The library had insert sizes ranging from 68 to 178 kb. We identified two recombinant BACs from the L. monocytogenes pUvBBAC library that each contained the entire virulence gene cluster (vgc) of L. monocytogenes and transferred them to a nonpathogenic Listeria innocua strain. Recombinant L. innocua strains harboring pUvBBAC+vgc1 and pUvBBAC+vgc2 produced the vgc-specific listeriolysin (LLO) and actin assembly protein ActA and represent the first reported cloning of the vgc locus in its entirety. The use of the novel broad-host-range BAC vector pUvBBAC extends the versatility of this technology and provides a powerful platform for detailed functional genomics of gram-positive bacteria as well as its use in explorative functional metagenomics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A genomic BAC library and a new BAC-GFP vector to study the holocentric pest Spodoptera frugiperda.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Apr;34(4):331-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2003.12.004. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15041017
-
Genome organization and the evolution of the virulence gene locus in Listeria species.Int J Med Microbiol. 2000 May;290(2):167-74. doi: 10.1016/S1438-4221(00)80086-7. Int J Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11045921 Review.
-
Comparative and functional genomics of Listeria spp.J Biotechnol. 2006 Oct 20;126(1):37-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.03.047. Epub 2006 Jun 6. J Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16757050 Review.
-
A genome-wide, end-sequenced 129Sv BAC library resource for targeting vector construction.Genomics. 2005 Dec;86(6):753-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.08.003. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16257172
-
Pathogenicity, genotyping and antibacterial susceptibility of the Listeria spp. recovered from stray dogs.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jan;126:123-133. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.10.037. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30381253
Cited by
-
Biotechnological applications of Listeria's sophisticated infection strategies.Microb Biotechnol. 2008 Sep;1(5):361-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2008.00037.x. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Microb Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 21261856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective immunity to Listeria monocytogenes infection mediated by recombinant Listeria innocua harboring the VGC locus.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035503. Epub 2012 Apr 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22536395 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous viral expression systems in fosmid vectors increase the functional analysis potential of metagenomic libraries.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1107. doi: 10.1038/srep01107. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23346364 Free PMC article.
-
Tools for functional postgenomic analysis of listeria monocytogenes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Jul;74(13):3921-34. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00314-08. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18441118 Free PMC article.
-
Improved cultivation and metagenomics as new tools for bioprospecting in cold environments.Extremophiles. 2015 Jan;19(1):17-29. doi: 10.1007/s00792-014-0704-3. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Extremophiles. 2015. PMID: 25399309 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barloy-Hubler, F., D. Capela, J. Batut, and F. Galibert. 2000. High-resolution physical map of the pSymb megaplasmid and comparison of the three replicons of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 1021. Curr. Microbiol. 41:109-113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

