HSP72 protects against obesity-induced insulin resistance
- PMID: 18223156
- PMCID: PMC2234214
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705799105
HSP72 protects against obesity-induced insulin resistance
Abstract
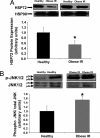
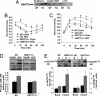
Patients with type 2 diabetes have reduced gene expression of heat shock protein (HSP) 72, which correlates with reduced insulin sensitivity. Heat therapy, which activates HSP72, improves clinical parameters in these patients. Activation of several inflammatory signaling proteins such as c-jun amino terminal kinase (JNK), inhibitor of kappaB kinase, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, can induce insulin resistance, but HSP 72 can block the induction of these molecules in vitro. Accordingly, we examined whether activation of HSP72 can protect against the development of insulin resistance. First, we show that obese, insulin resistant humans have reduced HSP72 protein expression and increased JNK phosphorylation in skeletal muscle. We next used heat shock therapy, transgenic overexpression, and pharmacologic means to overexpress HSP72 either specifically in skeletal muscle or globally in mice. Herein, we show that regardless of the means used to achieve an elevation in HSP72 protein, protection against diet- or obesity-induced hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance was observed. This protection was tightly associated with the prevention of JNK phosphorylation. These findings identify an essential role for HSP72 in blocking inflammation and preventing insulin resistance in the context of genetic obesity or high-fat feeding.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: We obtained the drug BGP-15 from N-Gene R&D Inc., and I.H., L.V., and M.A.F. have a financial interest in this company.
Figures
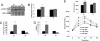
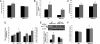
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002;288:1723–1727. - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature. 2006;444:860–867. - PubMed
-
- Watt MJ, Hevener A, Lancaster GI, Febbraio MA. Ciliary neurotrophic factor prevents acute lipid-induced insulin resistance by attenuating ceramide accumulation and phosphorylation of JNK in peripheral tissues. Endocrinology. 2006;147:2077–2085. - PubMed
-
- Hirosumi J, et al. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature. 2002;420:333–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

