Meta-analysis of 23 type 2 diabetes linkage studies from the International Type 2 Diabetes Linkage Analysis Consortium
- PMID: 18223311
- PMCID: PMC2855874
- DOI: 10.1159/000114164
Meta-analysis of 23 type 2 diabetes linkage studies from the International Type 2 Diabetes Linkage Analysis Consortium
Erratum in
- Hum Hered. 2008;66(4):237
Abstract
Background: The International Type 2 Diabetes Linkage Analysis Consortium was formed to localize type 2 diabetes predisposing variants based on 23 autosomal linkage scans.
Methods: We carried out meta-analysis using the genome scan meta-analysis (GSMA) method which divides the genome into bins of approximately 30 cM, ranks the best linkage results in each bin for each sample, and then sums the ranks across samples. We repeated the meta-analysis using 2 cM bins, and/or replacing bin ranks with measures of linkage evidence: bin maximum LOD score or bin minimum p value for bins with p value <0.05 (truncated p value). We also carried out computer simulations to assess the empirical type I error rates of these meta-analysis methods.
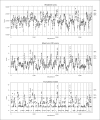
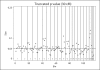
Results: Our analyses provided modest evidence for type 2 diabetes-predisposing variants on chromosomes 4, 10, and 14 (using LOD scores or truncated p values), or chromosome 10 and 16 (using ranks). Our simulation results suggested that uneven marker density across studies results in substantial variation in empirical type I error rates for all meta-analysis methods, but that 2 cM bins and scores that make more explicit use of linkage evidence, especially the truncated p values, reduce this problem.
Conclusion: We identified regions modestly linked with type 2 diabetes by summarizing results from 23 autosomal genome scans.
Copyright (c) 2008 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Bennett PH, Bogardus C, Tuomilehto J, Zimmett P. Epidemiology and natural history of NIDDM. In: Alberti KGMM, DeFronzo RA, Keen H, Zimmett P, editors. Nonobese and Obese. New York: Wiley; 1992. pp. 147–176.
-
- Hanis CL, Boerwinkle E, Chakraborty R, Ellsworth DL, Concannon P, Stirling B, Morrison VA, Wapelhorst B, Spielman RS, Gogolin-Ewens KJ, Shepard JM, Williams SR, Risch N, Hinds D, Iwasaki N, Ogata M, Omori Y, Petzold C, Rietzch H, Schroder HE, Schulze J, Cox NJ, Menzel S, Boriraj VV, Chen X, Lim LR, Lindner T, Mereu LE, Wang YQ, Xiang K, Yamagata K, Yang Y, Bell GI. A genome-wide search for human non-insulin-dependent (type 2) diabetes genes reveals a major susceptibility locus on chromosome 2. Nat Genet. 1996;13:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Mahtani MM, Widen E, Lehto M, Thomas J, McCarthy M, Brayer J, Bryant B, Chan G, Daly M, Forsblom C, Kanninen T, Kirby A, Kruglyak L, Munnelly K, Parkkonen M, Reeve-Daly MP, Weaver A, Brettin T, Duyk G, Lander ES, Groop LC. Mapping of a gene for type 2 diabetes associated with an insulin secretion defect by a genome scan in Finnish families. Nat Genet. 1996;14:90–94. - PubMed
-
- Zouali H, Hani E, Philippi A, Vionnet N, Beckmann J, Demenais F, Froguel P. A susceptibility locus for early-onset non-insulin dependent (type 2) diabetes mellitus maps to chromosome 20q, proximal to the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:1401–1408. - PubMed
-
- Hanson RL, Ehm MG, Pettitt DJ, Prochazka M, Thompson DB, Timberlake D, Foroud T, Kobes S, Baier L, Burns DK, Almasy L, Blangero J, Garvey WT, Bennett PH, Knowler WC. An autosomal genomic scan for loci linked to type II diabetes mellitus and body-mass index in Pima Indians. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63:1130–1138. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK072128/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK54261/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG000376/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK62370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MH59490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HG00376/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK47482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 3T37TW00041/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- DK72128/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL45522/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054261/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HG000376/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK54001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DK054001/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK058026/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- T37 TW000041/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL045522/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DK42273/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58026/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical