Bifunctional role of Rev-erbalpha in adipocyte differentiation
- PMID: 18227153
- PMCID: PMC2268425
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01608-07
Bifunctional role of Rev-erbalpha in adipocyte differentiation
Abstract
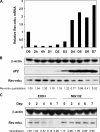
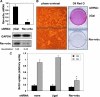
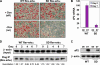
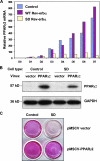
The nuclear receptor Rev-erbalpha is a potent transcriptional repressor that regulates circadian rhythm and metabolism. Here we demonstrate a dissociation between Rev-erbalpha mRNA and protein levels that profoundly influences adipocyte differentiation. During adipogenesis, Rev-erbalpha gene expression initially declines and subsequently increases. Remarkably, Rev-erbalpha protein levels are nearly the opposite, increasing early in adipogenesis and then markedly decreasing in adipocytes. The Rev-erbalpha protein is necessary for the early mitotic events that are required for adipogenesis. The subsequent reduction in Rev-erbalpha protein, due to increased degradation via the 26S proteasome, is also required for adipocyte differentiation because Rev-erbalpha represses the expression of PPARgamma2, the master transcriptional regulator of adipogenesis. Thus, opposite to what might be predicted from Rev-erbalpha gene expression, Rev-erbalpha protein levels must rise and then fall for adipocyte differentiation to occur.
Figures


References
-
- Ando, H., H. Yanagihara, Y. Hayashi, Y. Obi, S. Tsuruoka, T. Takamura, S. Kaneko, and A. Fujimura. 2005. Rhythmic messenger ribonucleic acid expression of clock genes and adipocytokines in mouse visceral adipose tissue. Endocrinology 1465631-5636. - PubMed
-
- Balsalobre, A., F. Damiola, and U. Schibler. 1998. A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells. Cell 93929-937. - PubMed
-
- Brady, M. J., F. J. Bourbonais, and A. R. Saltiel. 1998. The activation of glycogen synthase by insulin switches from kinase inhibition to phosphatase activation during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 27314063-14066. - PubMed
-
- Chawla, A., and M. A. Lazar. 1993. Induction of Rev-ErbAα, an orphan receptor encoded on the opposite strand of the α-thyroid hormone receptor gene, during adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 26816265-16269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
