Involvement of DPP-IV catalytic residues in enzyme-saxagliptin complex formation
- PMID: 18227430
- PMCID: PMC2222712
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.073253208
Involvement of DPP-IV catalytic residues in enzyme-saxagliptin complex formation
Abstract
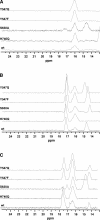
The inhibition of DPP-IV by saxagliptin has been proposed to occur through formation of a covalent but reversible complex. To evaluate further the mechanism of inhibition, we determined the X-ray crystal structure of the DPP-IV:saxagliptin complex. This structure reveals covalent attachment between S630 and the inhibitor nitrile carbon (C-O distance <1.3 A). To investigate whether this serine addition is assisted by the catalytic His-Asp dyad, we generated two mutants of DPP-IV, S630A and H740Q, and assayed them for ability to bind inhibitor. DPP-IV H740Q bound saxagliptin with an approximately 1000-fold reduction in affinity relative to DPP-IV WT, while DPP-IV S630A showed no evidence for binding inhibitor. An analog of saxagliptin lacking the nitrile group showed unchanged binding properties to the both mutant proteins, highlighting the essential role S630 and H740 play in covalent bond formation between S630 and saxagliptin. Further supporting mechanism-based inhibition by saxagliptin, NMR spectra of enzyme-saxagliptin complexes revealed the presence of three downfield resonances with low fractionation factors characteristic of short and strong hydrogen bonds (SSHB). Comparison of the NMR spectra of various wild-type and mutant DPP-IV:ligand complexes enabled assignment of a resonance at approximately 14 ppm to H740. Two additional DPP-IV mutants, Y547F and Y547Q, generated to probe potential stabilization of the enzyme-inhibitor complex by this residue, did not show any differences in inhibitor binding either by ITC or NMR. Together with the previously published enzymatic data, the structural and binding data presented here strongly support a histidine-assisted covalent bond formation between S630 hydroxyl oxygen and the nitrile group of saxagliptin.
Figures





References
-
- Aertgeerts, K., Ye, S., Tennant, M.G., Kraus, M.L., Rogers, J., Sang, B.-C., Skene, R.J., Webb, D.R., Prasad, G.S. Crystal structure of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV in complex with the decapeptide reveals details on substrate specificity and tetrahedral intermediate formation. Protein Sci. 2004;13:412–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahren, B., Simonsson, E., Larsson, H., Landin-Olson, M., Torgeirsson, H., Jansson, P.A., Sandquist, M., Bavenholm, P., Efendic, S., Eriksson, J.W. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV improves metabolic control over a 4-week study period in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:869–875. - PubMed
-
- Ahren, B., Gomis, R., Standl, E., Mills, D., Schweizer, A. Twelve- and 52-week efficacy of the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor LAF237 in metformin-treated patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2874–2888. - PubMed
-
- Ahren, B., Pacini, G., Foley, J.E., Schweizer, A. Improved meal-related β-cell function and insulin sensitivity by the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor vildagliptin in metformin-treated patients with Type 2 diabetes over 1 year. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1936–1940. - PubMed
-
- Augeri, D.J., Betebenner, D.A., Magnin, D.R., Robl, J.A., Khanna, A., Robertson, J.G., Wang, A., Simpkins, L.M., Taunk, P., Huang, Q., et al. Discovery and preclinical profile of saxagliptin (BMS-477118): A highly potent, long-acting, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2005;48:5025–5037. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

