The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP
- PMID: 18227510
- PMCID: PMC2538882
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0709662105
The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP
Abstract
Lung cancers caused by activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are initially responsive to small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), but the efficacy of these agents is often limited because of the emergence of drug resistance conferred by a second mutation, T790M. Threonine 790 is the "gatekeeper" residue, an important determinant of inhibitor specificity in the ATP binding pocket. The T790M mutation has been thought to cause resistance by sterically blocking binding of TKIs such as gefitinib and erlotinib, but this explanation is difficult to reconcile with the fact that it remains sensitive to structurally similar irreversible inhibitors. Here, we show by using a direct binding assay that T790M mutants retain low-nanomolar affinity for gefitinib. Furthermore, we show that the T790M mutation activates WT EGFR and that introduction of the T790M mutation increases the ATP affinity of the oncogenic L858R mutant by more than an order of magnitude. The increased ATP affinity is the primary mechanism by which the T790M mutation confers drug resistance. Crystallographic analysis of the T790M mutant shows how it can adapt to accommodate tight binding of diverse inhibitors, including the irreversible inhibitor HKI-272, and also suggests a structural mechanism for catalytic activation. We conclude that the T790M mutation is a "generic" resistance mutation that will reduce the potency of any ATP-competitive kinase inhibitor and that irreversible inhibitors overcome this resistance simply through covalent binding, not as a result of an alternative binding mode.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.J.E. and M.M. are consultants for and receive research funding from Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research.
Figures
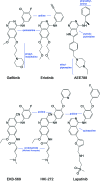
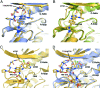
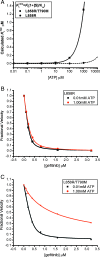
References
-
- Paez JG, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Johnson BE, Janne PA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7525–7529. - PubMed
-
- Gazdar AF, Shigematsu H, Herz J, Minna JD. Mutations and addiction to EGFR: The Achilles “heal” of lung cancers? Trends Mol Med. 2004;10:481–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

