New insights on COPD imaging via CT and MRI
- PMID: 18229568
- PMCID: PMC2695207
New insights on COPD imaging via CT and MRI
Abstract
Multidetector-row computed tomography (MDCT) can be used to quantify morphological features and investigate structure/function relationship in COPD. This approach allows a phenotypical definition of COPD patients, and might improve our understanding of disease pathogenesis and suggest new therapeutical options. In recent years, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has also become potentially suitable for the assessment of ventilation, perfusion and respiratory mechanics. This review focuses on the established clinical applications of CT, and novel CT and MRI techniques, which may prove valuable in evaluating the structural and functional damage in COPD.
Figures
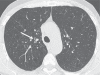

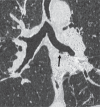
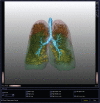
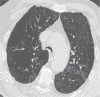

References
-
- Albert MS, Cates GD, Driehuys B, et al. Biological magnetic resonance imaging using laserpolarized 129Xe. Nature. 1994;370:199–201. - PubMed
-
- Amundsen T, Torheim G, Waage A, et al. Perfusion magnetic resonance imaging of the lung: characterization of pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A feasibility study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;12:224–31. - PubMed
-
- Aziz ZA, Wells AU, Desai SR, et al. Functional impairment in emphysema: contribution of airway abnormalities and distribution of parenchymal disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:1509–15. - PubMed
-
- Bankier AA, De Maertelar V, Keyzer C, et al. Pulmonary emphysema: subjective visual grading versus objective quantification with macroscopic morphometry and thin-section CT densitometry. Radiology. 1999;211:851–8. - PubMed
-
- Bayat S, Le DG, Porra L, et al. Quantitative functional lung imaging with synchrotron radiation using inhaled xenon as contrast agent. Phys Med Biol. 2001;46:3287–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

