Activation of p53-dependent responses in tumor cells treated with a PARC-interacting peptide
- PMID: 18230339
- PMCID: PMC7398582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.093
Activation of p53-dependent responses in tumor cells treated with a PARC-interacting peptide
Abstract
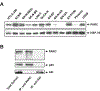
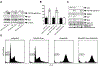
We tested the activity of a p53 carboxy-terminal peptide containing the PARC-interacting region in cancer cells with wild type cytoplasmic p53. Peptide delivery was achieved by fusing it to the TAT transduction domain (TAT-p53-C-ter peptide). In a two-hybrid assay, the tetramerization domain (TD) of p53 was necessary and sufficient to bind PARC. The TAT-p53-C-ter peptide disrupted the PARC-p53 complex. Peptide treatment caused p53 nuclear relocation, p53-dependent changes in gene expression and enhancement of etoposide-induced apoptosis. These studies suggest that PARC-interacting peptides are promising candidates for the enhancement of p53-dependent apoptosis in tumors with wt cytoplasmic p53.
Figures


References
-
- Soussi T, Kato S, Levy PP, Ishioka C, Reassessment of the TP53 mutation database in human disease by data mining with a library of TP53 missense mutations Hum. Mutat 25 (2005) 6–17. - PubMed
-
- Nikolaev AY, Li M, Puskas N, Qin J, Gu W, Parc: a cytoplasmic anchor for p53 Cell 112 (2003) 29–40. - PubMed
-
- Kasper JS, Arai T, DeCaprio JA, A novel p53-binding domain in CUL7 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 348 (2006) 132–138. - PubMed
-
- Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, Fotouhi N, Liu EA, In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2 Science 303 (2004) 844–848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

