Differential expression of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and IGF-I pathway activation in human uterine leiomyomas
- PMID: 18231572
- PMCID: PMC2215764
- DOI: 10.2119/2007-00101.Yu
Differential expression of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and IGF-I pathway activation in human uterine leiomyomas
Erratum in
- Mol Med. 2008 Jul-Aug;14(7-8):538
Abstract
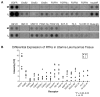
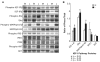
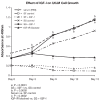
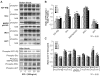
Uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) are benign tumors that are prevalent in women of reproductive age. Research suggests that activated receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) play an important role in the enhanced proliferation observed in fibroids. In this study, a phospho-RTK array technique was used to detect RTK activity in leiomyomas compared with myometrial tissue. We found that fifteen out of seventeen RTKs evaluated in this study were highly expressed (P < 0.02-0.03) in the leiomyomas, and included the IGF-I/IGF-IR, EGF/EGFR, FGF/FGF-R, HGF/HGF-R, and PDGF/PDGF-R gene families. Due to the higher protein levels of IGF-IR observed in leiomyomas by us in earlier studies, we decided to focus on the activation of the IGF-IR, its downstream effectors, and MAPKp44/42 to confirm our earlier findings; and validate the significance of the increased IGF-IR phosphorylation observed by RTK array analysis in this study. We used immunolocalization, western blot, or immunoprecipitation studies and confirmed that leiomyomas overexpressed IGF-IRbeta and phosphorylated IGF-IRbeta. Additionally, we showed that the downstream effectors, Shc, Grb2, and MAPKp44/42 (P < 0.02-0.001) were also overexpressed and involved in IGF-IR signaling in these tumors, while IRS-I, PI3K, and AKT were not. In vitro studies showed that IGF-I (100 ng/mL) increased the proliferation of uterine leiomyoma cells (UtLM) (P < 0.0001), and that phosphorylated IGF-IRbeta, Shc, and MAPKp44/42 were also overexpressed in IGF-I-treated UtLM cells (P < 0.05), similar to the tissue findings. A neutralizing antibody against the IGF-IRbeta blocked these effects. These data indicate that overexpression of RTKs and, in particular, activation of the IGF-IR signaling pathway through Shc/Grb2/MAPK are important in mediating uterine leiomyoma growth. These data may provide new anti-tumor targets for noninvasive treatment of fibroids.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases and their hormonal regulation in uterine leiomyoma.Semin Reprod Med. 2010 May;28(3):250-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1251482. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Semin Reprod Med. 2010. PMID: 20414848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemical localization of growth factors and their receptors in uterine leiomyomas and matched myometrium.Environ Health Perspect. 2000 Oct;108 Suppl 5:795-802. doi: 10.1289/ehp.00108s5795. Environ Health Perspect. 2000. PMID: 11035985
-
Increased insulin sensitivity in IGF-I receptor--deficient brown adipocytes.Diabetes. 2002 Mar;51(3):743-54. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.3.743. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 11872675
-
Tamoxifen interferes with the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) signaling pathway in breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 1997 Jul 1;57(13):2606-10. Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9205064
-
Review: The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Signaling Pathways in Uterine Leiomyoma.In Vivo. 2015 Nov-Dec;29(6):637-49. In Vivo. 2015. PMID: 26546520 Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in uterine leiomyoma: role in tumor biology and targeting opportunities.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Sep;476(9):3513-3536. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04174-6. Epub 2021 May 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33999334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix production and remodeling as therapeutic targets for uterine leiomyoma.J Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Sep;8(3):179-94. doi: 10.1007/s12079-014-0234-x. Epub 2014 Jul 11. J Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 25012731 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases and their hormonal regulation in uterine leiomyoma.Semin Reprod Med. 2010 May;28(3):250-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1251482. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Semin Reprod Med. 2010. PMID: 20414848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proceedings from the Third National Institutes of Health International Congress on Advances in Uterine Leiomyoma Research: comprehensive review, conference summary and future recommendations.Hum Reprod Update. 2014 May-Jun;20(3):309-33. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmt058. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Hum Reprod Update. 2014. PMID: 24401287 Free PMC article.
-
The androgen receptor mediates antiapoptotic function in myometrial cells.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jul 17;5(7):e1338. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.303. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25032861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mauskopf J, Flynn M, Thieda P, Spalding J, Duchane J. The economic impact of uterine fibroids in the United States: a summary of published estimates. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2005;14:692–703. - PubMed
-
- Wallach EE, Vlahos NF. Uterine myomas: an overview of development, clinical features, and management. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;104:393–406. - PubMed
-
- Bennasroune A, Gardin A, Aunis D, Cremel G, Hubert P. Tyrosine kinase receptors as attractive targets of cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2004;50:23–38. - PubMed
-
- Dixon D, He H, Haseman JK. Immunohistochemical localization of growth factors and their receptors in uterine leiomyomas and matched myometrium. Environ Health Perspect. 2000;5(108 Suppl):795–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

