Emodin-induced generation of reactive oxygen species inhibits RhoA activation to sensitize gastric carcinoma cells to anoikis
- PMID: 18231637
- PMCID: PMC2213898
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.07754
Emodin-induced generation of reactive oxygen species inhibits RhoA activation to sensitize gastric carcinoma cells to anoikis
Abstract
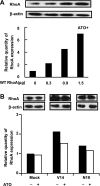
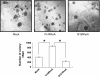
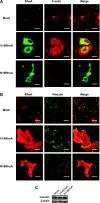
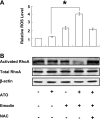
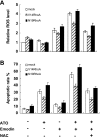
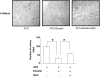
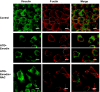
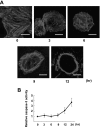
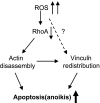
RhoA is a critical signaling molecule regulating a variety of cellular processes, such as cytoskeletal organization, adhesion, and apoptosis. It is recently considered responsive to reactive oxygen species (ROS). Nevertheless, how RhoA regulates anoikis, a detachment-initiated apoptosis, and how this regulation is affected by ROS are not clear. The present study investigated the role of RhoA in apoptosis/anoikis in gastric cancer cells and the changes of RhoA and anoikis under oxidative stress. Immunohistochemistry showed that RhoA expression was upregulated in the primary gastric carcinoma compared with normal gastric mucosa. Overactivation of RhoA by transfection with the V14RhoA mutant prevented gastric cancer line SGC-7901 cells from arsenic-induced apoptosis and conferred anoikis resistance through, at least in part, promoting formations of F-actin fibers and focal adhesion. Oxidative stress caused by emodin, an ROS producer, in combination with arsenic trioxide (ATO) led to RhoA inactivation that triggered structural disruption of focal adhesion complex and eventually resulted in anoikis, and these effects could be partially reversed by antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC). In conclusion, activation of RhoA is required for the maintenance of anoikis resistance phenotype of gastric cancer cells, and oxidative stress might be a therapeutic strategy for the inhibition of RhoA in cancer cells.
Figures
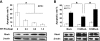
References
-
- Hall A. RhoA GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279:509–514. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ. Rho family proteins: coordinating cell responses. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2001;11:471–477. - PubMed
-
- Coleman ML, Olson MF. Rho GTPase signaling pathways in the morphological changes associated with apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2002;9:493–504. - PubMed
-
- Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 2002;420:629–635. - PubMed
-
- Vega FM, Ridley AJ. SnapShot: Rho Family GTPases. Cell. 2007;129:1430–1431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
