Spatially and temporally resolved single-cell exocytosis utilizing individually addressable carbon microelectrode arrays
- PMID: 18232712
- PMCID: PMC2653425
- DOI: 10.1021/ac702409s
Spatially and temporally resolved single-cell exocytosis utilizing individually addressable carbon microelectrode arrays
Abstract
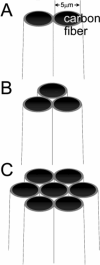
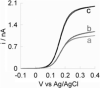
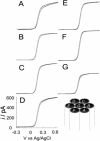
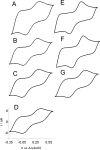
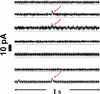
We report the fabrication and characterization of carbon microelectrode arrays (MEAs) and their application to spatially and temporally resolve neurotransmitter release from single pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. The carbon MEAs are composed of individually addressable 2.5-mum-radius microdisks embedded in glass. The fabrication involves pulling a multibarrel glass capillary containing a single carbon fiber in each barrel into a sharp tip, followed by beveling the electrode tip to form an array (10-20 microm) of carbon microdisks. This simple fabrication procedure eliminates the need for complicated wiring of the independent electrodes, thus allowing preparation of high-density individually addressable microelectrodes. The carbon MEAs have been characterized using scanning electron microscopy, steady-state and fast-scan voltammetry, and numerical simulations. Amperometric results show that subcellular heterogeneity in single-cell exocytosis can be electrochemically detected with MEAs. These ultrasmall electrochemical probes are suitable for detecting fast chemical events in tight spaces, as well as for developing multifunctional electrochemical microsensors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Simultaneous study of subcellular exocytosis with individually addressable multiple microelectrodes.Analyst. 2014 Jul 7;139(13):3290-5. doi: 10.1039/c4an00058g. Analyst. 2014. PMID: 24740449
-
Carbon-ring microelectrode arrays for electrochemical imaging of single cell exocytosis: fabrication and characterization.Anal Chem. 2012 Mar 20;84(6):2949-54. doi: 10.1021/ac3000368. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22339586 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial resolution of single-cell exocytosis by microwell-based individually addressable thin film ultramicroelectrode arrays.Anal Chem. 2014 May 6;86(9):4515-20. doi: 10.1021/ac500443q. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Anal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24712854 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in Flexible Microelectrode Arrays for Combined Electrophysiological and Electrochemical Sensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 10;15(2):100. doi: 10.3390/bios15020100. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical analysis of single cells and exocytosis.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1997;11(1):59-90. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v11.i1.40. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1997. PMID: 9093814 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct electrochemical observation of glucosidase activity in isolated single lysosomes from a living cell.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Apr 17;115(16):4087-4092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1719844115. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29610324 Free PMC article.
-
Collection of peptides released from single neurons with particle-embedded monolithic capillaries followed by detection with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2011 Dec 15;83(24):9557-63. doi: 10.1021/ac202338e. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 22053721 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced real-time recordings of neuronal activity with tailored patch pipettes, diamond multi-electrode arrays and electrochromic voltage-sensitive dyes.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Jan;473(1):15-36. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02472-4. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 33047171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of electrochemical methods for tonic dopamine detection in vivo.Trends Analyt Chem. 2020 Nov;132:116049. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.116049. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Trends Analyt Chem. 2020. PMID: 33597790 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical analysis of single cells.Anal Chem. 2011 Jun 15;83(12):4369-92. doi: 10.1021/ac2009838. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21500835 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM. Principles of Neural Science. 4th ed. McGraw Hill; New York: 2000.
-
- Weber T, Zemelman BV, McNew JA, Westermann B, Gmachl M, Parlati F, Sollner TH, Rothman JF. Cell. 1998;92:759. - PubMed
-
- Chen TK, Luo G, Ewing AG. Anal. Chem. 1994;66:3031. - PubMed
-
- Wightman RM. Science. 2006;311:1570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

