Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators
- PMID: 18233953
- PMCID: PMC2739396
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.151409
Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators
Abstract
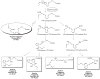
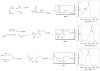
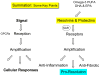
The popular view that all lipid mediators are pro-inflammatory arises largely from the finding that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block the biosynthesis of prostaglandins. The resolution of inflammation was widely held as a passive event until recently, with the characterization of novel biochemical pathways and lipid-derived mediators that are actively turned on in resolution and that possess potent anti-inflammatory and proresolving actions. A lipid-mediator informatics approach was employed to systematically identify new families of endogenous local-acting mediators from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) in resolving exudates, which also contain lipoxins and aspirin-triggered lipoxins generated from arachidonic acid. Given their potent bioactions, these new chemical mediator families were termed resolvins and protectins. Here, we review the recent advances in our understanding of the biosynthesis and stereospecific actions of these new proresolving mediators, which have also proven to be organ protective and antifibrotic.
Figures








References
-
- Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co; 1999. p. 1425.
-
- Levy BD, Clish CB, Schmidt B, Gronert K, Serhan CN. Lipid mediator class switching during acute inflammation: signals in resolution. Nature Immunol. 2001;2:612–19. This is the original report demonstrating temporal separation between individual classes of eicosanoids, i.e., dissociation between the formation and actions of prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and lipoxins in resolution. - PubMed
-
- Calder PC. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammation. Scand J Food Nutr. 2006;50(S2):54–61.
-
- Serhan CN, editor. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 3–4. Vol. 73. 2005. Special Issue on Lipoxins and Aspirin-Triggered Lipoxins; pp. 139–321. This special issue features nineteen reviews by experts covering the anti-inflammatory actions of lipoxins, aspirin-triggered lipoxins, and therapeutic potential of stable metabolic analogs. This is a detailed resource for original research and critical review of results on lipoxins and their mechanism of action. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

