Reduced albuminuria with sarpogrelate is accompanied by a decrease in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 18235151
- PMCID: PMC2390947
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03450807
Reduced albuminuria with sarpogrelate is accompanied by a decrease in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background and objectives: Sarpogrelate has been shown to reduce albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. For examination of whether this is based on the same mechanisms as angiotensin II receptor blockers or thiazolidinedione, effects of sarpogrelate on atherosclerotic inflammatory molecules and their relations to albuminuria in patients who had diabetes and had already been treated with angiotensin II receptor blockers and with or without thiazolidinedione were examined.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Forty patients who had diabetes with nephropathy and arteriosclerosis obliterans and had already been treated with angiotensin II receptor blocker (n = 40) were randomly assigned to sarpogrelate (300 mg/d; n = 20) or aspirin group (100 mg/d; n = 20). Plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 were measured at baseline and 16 wk after administration.
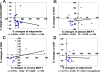
Results: Only the sarpogrelate group showed increases in plasma adiponectin and decreases in both plasma and urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and albumin-to-creatinine ratio levels. Moreover, percentage change of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 level correlated positively to that of albumin-to-creatinine ratio. Even when the sarpogrelate group was further divided into two groups with (n = 9) or without thiazolidinedione (n = 11), changes in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 or albumin-to-creatinine ratio did not differ.
Conclusions: Sarpogrelate can reduce albuminuria and plasma and urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels while increasing plasma adiponectin in diabetic nephropathy. These effects seem to be mediated via mechanisms that are different from those of angiotensin II receptor blocker or thiazolidinedione.
Figures

References
-
- Doggrell SA: Sarpogrelate: Cardiovascular and renal clinical potential. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 13: 865–874, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Ogawa S, Takeuchi K, Sugimura K, Sato C, Fukuda M, Lee R, Ito S, Sato T: The 5-HT2 receptor antagonist sarpogrelate reduces urinary and plasma levels of thromboxane A2 and urinary albumin excretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26: 461–464, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Ibsen H, Olsen MH, Wachtell K, Borch-Johnsen K, Lindholm LH, Mogensen CE, Dahlof B, Snapinn SM, Wan Y, Lyle PA: Does albuminuria predict cardiovascular outcomes on treatment with losartan versus atenolol in patients with diabetes, hypertension, and left ventricular hypertrophy? The LIFE study. Diabetes Care 29: 595–600, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Grewal JS, Mukhin YV, Garnovskaya MN, Raymond JR, Greene EL: Serotonin %-HT2A receptor induces TGF-beta1 expression in mesangial cells via ERK: Proliferative and fibrotic signals. Am J Physiol 276: F922–F930, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Kasho M, Sakai M, Sasahara T, Anami Y, Matsumura T, Takemura T, Matsuda H, Kobori S, Shichiri M: Serotonin enhances the production of type IV collagen by human mesangial cells. Kidney Int 54: 1083–1092, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

