Minimally invasive repair of traumatic right-sided diaphragmatic hernia with delayed diagnosis
- PMID: 18237515
- PMCID: PMC3015846
Minimally invasive repair of traumatic right-sided diaphragmatic hernia with delayed diagnosis
Abstract
Background: Traumatic diaphragmatic hernias are a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge due to variable presentations. Early repair is important because of risks of incarceration and strangulation of abdominal contents along with respiratory and cardiovascular compromise. Minimally invasive techniques have been useful for diagnosis and treatment of diaphragmatic hernias in both blunt and penetrating trauma.
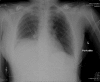
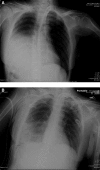
Method: We present the case of a 54-year-old victim of a motor vehicle crash who presented with a delayed diagnosis of a right-sided traumatic diaphragmatic hernia. By using a 4-port technique and intracorporeal suturing, the hernia was repaired. This case highlights the difficulties associated with diagnosing diaphragmatic hernias and the role of minimally invasive techniques to repair them.
Conclusion: Minimally invasive surgical techniques are being increasingly used to both diagnose and repair traumatic diaphragmatic injuries with excellent results.
Figures





References
-
- Eren S, Kantarci M, Okur A. Imaging of diaphragmatic rupture after trauma. Clin Radiol. 2006;61(6):467–477 - PubMed
-
- Kaw LL, Jr., Potenza BM, Coimbra R, Hoyt DB. Traumatic diaphragmatic hernia. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198(4):668–669 - PubMed
-
- Sirbu H, Busch T, Spillner J, Schachtrupp A, Autschbach R. Late bilateral diaphragmatic rupture: challenging diagnostic and surgical repair. Hernia. 2005;9(1):90–92 - PubMed
-
- Baglaj M, Dorobisz U. Late-presenting congenital diaphragmatic hernia in children: a literature review. Pediatr Radiol. 2005;35(5):478–488 - PubMed
-
- Christie D, Chapman J, Wynne J, Ashley D. Delayed right-sided diaphragmatic hernia and chronic herniation of unusual abdominal contents. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204(1):176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
