Stat5 activation enables erythropoiesis in the absence of EpoR and Jak2
- PMID: 18239084
- PMCID: PMC2976848
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-07-102848
Stat5 activation enables erythropoiesis in the absence of EpoR and Jak2
Abstract
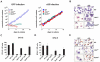
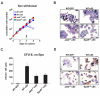
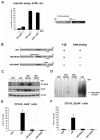
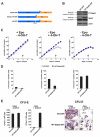
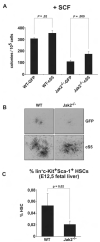
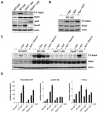
Erythropoiesis requires erythropoietin (Epo) and stem cell factor (SCF) signaling via their receptors EpoR and c-Kit. EpoR, like many other receptors involved in hematopoiesis, acts via the kinase Jak2. Deletion of EpoR or Janus kinase 2 (Jak2) causes embryonic lethality as a result of defective erythropoiesis. The contribution of distinct EpoR/Jak2-induced signaling pathways (mitogen-activated protein kinase, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 [Stat5]) to functional erythropoiesis is incompletely understood. Here we demonstrate that expression of a constitutively activated Stat5a mutant (cS5) was sufficient to relieve the proliferation defect of Jak2(-/-) and EpoR(-/-) cells in an Epo-independent manner. In addition, tamoxifen-induced DNA binding of a Stat5a-estrogen receptor (ER)* fusion construct enabled erythropoiesis in the absence of Epo. Furthermore, c-Kit was able to enhance signaling through the Jak2-Stat5 axis, particularly in lymphoid and myeloid progenitors. Although abundance of hematopoietic stem cells was 2.5-fold reduced in Jak2(-/-) fetal livers, transplantation of Jak2(-/-)-cS5 fetal liver cells into irradiated mice gave rise to mature erythroid and myeloid cells of donor origin up to 6 months after transplantation. Cytokine- and c-Kit pathways do not function independently of each other in hematopoiesis but cooperate to attain full Jak2/Stat5 activation. In conclusion, activated Stat5 is a critical downstream effector of Jak2 in erythropoiesis/myelopoiesis, and Jak2 functionally links cytokine- with c-Kit-receptor tyrosine kinase signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Richmond TD, Chohan M, Barber DL. Turning cells red: signal transduction mediated by erythropoietin. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:146–155. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Sytkowski AJ. Erythropoietin regulation of Raf-1 and MEK: evidence for a Ras-independent mechanism. Blood. 2004;104:73–80. - PubMed
-
- von Lindern M, Parren-van Amelsvoort M, van Dijk T, et al. Protein kinase C alpha controls erythropoietin receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:34719–34727. - PubMed
-
- Tong Q, Chu X, Cheung JY, et al. Erythropoietin-modulated calcium influx through TRPC2 is mediated by phospholipase Cgamma and IP3R. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;287:C1667–1678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

