Systemic leukocyte-directed siRNA delivery revealing cyclin D1 as an anti-inflammatory target
- PMID: 18239128
- PMCID: PMC2490797
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1149859
Systemic leukocyte-directed siRNA delivery revealing cyclin D1 as an anti-inflammatory target
Abstract
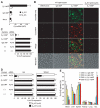
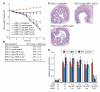
Cyclin D1 (CyD1) is a pivotal cell cycle-regulatory molecule and a well-studied therapeutic target for cancer. Although CyD1 is also strongly up-regulated at sites of inflammation, its exact roles in this context remain uncharacterized. To address this question, we developed a strategy for selectively silencing CyD1 in leukocytes in vivo. Targeted stabilized nanoparticles (tsNPs) were loaded with CyD1-small interfering RNA (siRNA). Antibodies to beta(7) integrin (beta(7) I) were then used to target specific leukocyte subsets involved in gut inflammation. Systemic application of beta(7) I-tsNPs silenced CyD1 in leukocytes and reversed experimentally induced colitis in mice by suppressing leukocyte proliferation and T helper cell 1 cytokine expression. This study reveals CyD1 to be a potential anti-inflammatory target, and suggests that the application of similar modes of targeting by siRNA may be feasible in other therapeutic settings.
Figures
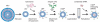
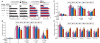
Comment in
-
Molecular biology. The art of assembly.Science. 2008 Feb 1;319(5863):578-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1154253. Science. 2008. PMID: 18239114 No abstract available.
References
-
- Iorns E, Lord CJ, Turner N, Ashworth A. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007;6:556. - PubMed
-
- Stacey DW. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003;15:158. - PubMed
-
- Fu M, Wang C, Li Z, Sakamaki T, Pestell RG. Endocrinology. 2004;145:5439. - PubMed
-
- Yang R, Bie W, Haegebarth A, Tyner AL. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:180. - PubMed
-
- van Dekken H, et al. Acta Histochem. 2007;109:266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

