Association of the FTO gene with BMI
- PMID: 18239580
- PMCID: PMC4476623
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2007.126
Association of the FTO gene with BMI
Abstract
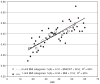
Variants in the FTO gene have been strongly associated with obesity in a very large sample (38,759) of diabetic and control subjects. To replicate these findings, the previously reported SNP in the FTO gene (rs9939609, T/A) was genotyped in 5,607 subjects from five different Utah studies. The studies included a random sample of the Utah population, families selected for aggregation of extreme thinness, families selected for severe obesity, a series of unrelated severe obesity subjects, and families participating in a 25-year longitudinal study of cardiovascular disease and aging. Results show a strong significant increase in the rs9939609 A allele frequency with increasing BMI (P < 0.0001). In the longitudinal study, FTO genotypes were significantly associated with BMI at a baseline exam, a 2(1/2)-year follow-up exam and a 25-year follow-up exam using an additive genetic model. The mean genotype difference in BMI ranged from 1.3 to 2.1 kg/m(2) across exams. The genotype difference in BMI means was established in youth, and at-risk subjects under age 20 at baseline had a significantly larger 25-year BMI increase (10.0 for A/A; 9.7 for A/T, and 8.5 kg/m(2) for T/T, P = 0.05). We conclude that the BMI increases associated with FTO genotypes begin in youth and are maintained throughout adulthood.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polymorphisms in the NPY2R gene show significant associations with BMI that are additive to FTO, MC4R, and NPFFR2 gene effects.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011 Nov;19(11):2241-7. doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.239. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011. PMID: 21818152 Free PMC article.
-
The common FTO variant rs9939609 is not associated with BMI in a longitudinal study on a cohort of Swedish men born 1920-1924.BMC Med Genet. 2009 Dec 9;10:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-131. BMC Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 20003232 Free PMC article.
-
Education modulates the association of the FTO rs9939609 polymorphism with body mass index and obesity risk in the Mediterranean population.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012 Aug;22(8):651-8. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 21186106 Free PMC article.
-
The common variant in the FTO gene did not modify the effect of lifestyle changes on body weight: the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009 Apr;17(4):832-6. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.618. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009. PMID: 19180072 Clinical Trial.
-
Piecing together the FTO jigsaw.Genome Biol. 2011;12(2):104. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-2-104. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 21349207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A randomized trial of the clinical utility of genetic testing for obesity: design and implementation considerations.Clin Trials. 2014 Feb;11(1):102-13. doi: 10.1177/1740774513508029. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Clin Trials. 2014. PMID: 24216219 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Obesity-associated gene FTO rs9939609 polymorphism in relation to the risk of tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Nov 7;14:592. doi: 10.1186/s12879-014-0592-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25377722 Free PMC article.
-
No Influence of the Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Gene rs9939609 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism on Blood Lipids in Young Males.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 17;12(12):3857. doi: 10.3390/nu12123857. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33348678 Free PMC article.
-
The epithelial sodium channel γ-subunit gene and blood pressure: family based association, renal gene expression, and physiological analyses.Hypertension. 2011 Dec;58(6):1073-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.176370. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Hypertension. 2011. PMID: 22006290 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of FTO genotypes on BMI and weight in polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetologia. 2012 Oct;55(10):2636-2645. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2638-6. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22801903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dina C, Meyre D, Gallina S, et al. Variation in FTO contributes to childhood obesity and severe adult obesity. Nat Genet. 2007;39:724–726. - PubMed
-
- Hunt SC, Xin Y, Wu LL, Hopkins PN, Adams TD. Lack of association of glutamate decarboxylase 2 gene polymorphisms with severe obesity in Utah. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006;14:650–655. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

