QTL for body composition on chromosome 7 detected using a chromosome substitution mouse strain
- PMID: 18239664
- PMCID: PMC2266090
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2007.26
QTL for body composition on chromosome 7 detected using a chromosome substitution mouse strain
Erratum in
- Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Jun;16(6):1476
- Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Sep;16(9):2190
Abstract
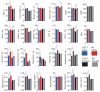
Objective: Previous studies in mice have detected quantitative trait loci (QTLs) on chromosome 7 that affect body composition. As a step toward identifying the responsible genes, we compared a chromosome 7 substitution strain C57BL/6J-Chr7(129S1/SvImJ)/Na (CSS-7) to its host (C57BL/6J) strain.
Methods and procedures: Fourteen-week-old mice were measured for body size (weight, length), organ weight (brain, heart, liver, kidneys, and spleen), body and bone composition (fat and lean weight; bone area, mineral content, and density), and individual adipose depot weights (gonadal, retroperitoneal, mesenteric, inguinal, and subscapular). Differences between the CSS-7 strain and the host strain were interpreted as evidence for the presence of one or more QTLs on chromosome 7.
Results: Using this criterion, we detected QTLs for body weight, bone area, bone mineral content, brain, and heart weight, most adipose depot weights and some indices of fatness. A few strain differences were more pronounced in males (e.g., most adiposity measures) and others were more pronounced in females (e.g., bone area). QTLs for body length, lean weight, bone mineral density, and kidney, spleen, and liver weight were not detected.
Discussion: This study found several associations that suggest one or more QTLs specific to the weight of select tissues and organs exist on mouse chromosome 7. Because these loci are detectable on a fixed and uniform genetic background, they are reasonable targets for high-resolution mapping and gene identification using a congenic approach.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
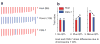
Similar articles
-
Body Composition QTLs Identified in Intercross Populations Are Reproducible in Consomic Mouse Strains.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 9;10(11):e0141494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141494. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26551037 Free PMC article.
-
A growth QTL (Pbwg1) region of mouse chromosome 2 contains closely linked loci affecting growth and body composition.Mamm Genome. 2007 Apr;18(4):229-39. doi: 10.1007/s00335-007-9009-5. Epub 2007 May 19. Mamm Genome. 2007. PMID: 17514348
-
Quantitative trait loci for individual adipose depot weights in C57BL/6ByJ x 129P3/J F2 mice.Mamm Genome. 2006 Nov;17(11):1065-77. doi: 10.1007/s00335-006-0054-2. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Mamm Genome. 2006. PMID: 17103053 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of QTL with major effects on fatness and growth on mouse chromosome 2.Obes Res. 2004 Sep;12(9):1408-20. doi: 10.1038/oby.2004.177. Obes Res. 2004. PMID: 15483205
-
A novel strategy for genetic dissection of complex traits: the population of specific chromosome substitution strains from laboratory and wild mice.Mamm Genome. 2010 Aug;21(7-8):370-6. doi: 10.1007/s00335-010-9270-x. Epub 2010 Jul 11. Mamm Genome. 2010. PMID: 20623355 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic analysis of abdominal fat distribution in SM/J and A/J mice.J Lipid Res. 2010 Dec;51(12):3463-9. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M009563. Epub 2010 Aug 27. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20802160 Free PMC article.
-
The Genetic Elements of the Obesity Paradox in Atherosclerosis Identified in an Intercross Between Hyperlipidemic Mouse Strains.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 29;26(9):4241. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094241. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362477 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of litter size in mice.J Vet Med Sci. 2015 Mar;77(3):353-8. doi: 10.1292/jvms.14-0350. Epub 2014 Nov 26. J Vet Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25428703 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait and transcriptome analysis of genetic complexity underpinning cardiac interatrial septation in mice using an advanced intercross line.Elife. 2023 Jun 5;12:e83606. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83606. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37272612 Free PMC article.
-
Body Composition QTLs Identified in Intercross Populations Are Reproducible in Consomic Mouse Strains.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 9;10(11):e0141494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141494. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26551037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kenney-Hunt JP, Vaughn TT, Pletscher LS, et al. Quantitative trait loci for body size components in mice. Mamm Genome. 2006;17(6):526–37. - PubMed
-
- Danforth C. Hereditary adiposity in mice. J Hered. 1927;18:153–162.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

