Results of treatment of patients with superficial facial rhabdomyosarcomas on protocols of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG), 1984-1997
- PMID: 18240175
- PMCID: PMC3357210
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.21447
Results of treatment of patients with superficial facial rhabdomyosarcomas on protocols of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG), 1984-1997
Abstract
Purpose: We analyzed the outcome of 47 patients with superficial facial rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) treated on Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG) Protocols-III, -IV-Pilot, and -IV.
Methods: We reviewed patients' records. Clinico-pathologic features, treatment, and outcome were examined to identify prognostic factors.
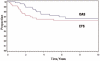
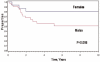
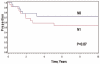
Results: Thirty-two patients were males; 35 patients were 1-9 years old at diagnosis. Tumor sites were buccal/cheek (N = 21), external nasal/nasolabial (N = 12), lip/chin (N = 9), and masseter (N = 5). Patients (46/47) had localized disease: 18 biopsy only (Group III), 17 microscopic residual tumor (Group II), and 11 complete resection without residual tumor (Group I). Eight-year estimated event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OAS) rates were 61% and 65%. Patients <12 months old had inferior EFS, 21%, compared to approximately 68% in older patients (P = 0.077). Eight-year EFS rates were 80% for females and 50% for males (P = 0.096). Eight-year EFS rates were 72% in 33 patients without regional lymph-nodal tumor and 39% in 14 patients with regional nodal tumor (P = 0.07). Eight-year EFS rates were 72% for 22 patients with embryonal RMS and 53% for 23 patients with alveolar RMS (P = 0.28). Location of the primary tumor was not significantly related to outcome.
Conclusions: Patients with superficial facial RMS often have localized, grossly resectable lesions at the time of presentation. Favorable prognostic factors include age >12 months, female gender, embryonal histology, and no lymph-nodal tumor.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance and tumor biology of regional lymph node disease in patients with rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Children's Oncology Group.J Clin Oncol. 2011 Apr 1;29(10):1304-11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.29.4611. Epub 2011 Feb 28. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21357792 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does debulking improve survival rate in advanced-stage retroperitoneal embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma?J Pediatr Surg. 1999 May;34(5):736-41; discussion 741-2. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(99)90366-4. J Pediatr Surg. 1999. PMID: 10359174
-
[Clinical and prognostic analysis of single-center multidisciplinary treatment for rhabdomyosarcoma in children].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Oct 2;57(10):767-773. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2019.10.008. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31594063 Chinese.
-
Volumetric considerations in radiotherapy for pediatric parameningeal rhabdomyosarcomas.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Apr 1;55(5):1294-9. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)04290-6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 12654440 Review.
-
Prognostic factors and surgical treatment guidelines for children with rhabdomyosarcoma of the perineum or anus: a report of Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Studies I through IV, 1972 through 1997.J Pediatr Surg. 2003 Mar;38(3):347-53. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2003.50106. J Pediatr Surg. 2003. PMID: 12632347 Review.
Cited by
-
Nonorbital, Nonparameningeal Head and Neck Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2025 Jun;72(6):e31673. doi: 10.1002/pbc.31673. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40108481
-
Rare adult masseteric rhabdomyosarcoma and a review of the literature.Case Rep Oncol. 2013 Sep 14;6(3):472-9. doi: 10.1159/000355250. eCollection 2013. Case Rep Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24163663 Free PMC article.
-
Sinonasal Tract Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma in Adults: A Clinicopathologic and Immunophenotypic Study of Fifty-Two Cases with Emphasis on Epithelial Immunoreactivity.Head Neck Pathol. 2018 Jun;12(2):181-192. doi: 10.1007/s12105-017-0851-9. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Head Neck Pathol. 2018. PMID: 28875443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maurer HM, Beltangady M, Gehan EA, et al. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-I. A final report. Cancer. 1988:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Maurer HM, Gehan EA, Beltangady M, et al. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-II. Cancer. 1993;71:1904–1922. - PubMed
-
- Crist WM, Raney RB, Ragab A, et al. Intensive chemotherapy including cisplatin with or without etoposide for children with soft-tissue sarcomas. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1987;15:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Crist W, Gehan EA, Ragab AH, et al. The Third Inter-group Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:610–630. - PubMed
-
- Ortega JA, Ragab AH, Gehan EA, et al. A feasibility, toxicity, and efficacy study of ifosfamide, actinomycin D, and vincristine for the treatment of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A report of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV Pilot Study. Am J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol. 1993;15:S15–S20.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

