Toothpick impaction with sigmoid colon pseudodiverticulum formation successfully treated with colonoscopy
- PMID: 18240357
- PMCID: PMC2687067
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.948
Toothpick impaction with sigmoid colon pseudodiverticulum formation successfully treated with colonoscopy
Abstract
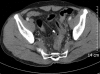
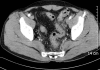
Foreign bodies in the colon are encountered with increasing frequency, but only sporadic reports concerning their management have appeared in the literature. While most ingested foreign bodies usually pass through the gastrointestinal tract uneventfully, sharp foreign bodies such as toothpicks infrequently cause intestinal perforation and may even result in death. We report our experience with a patient with a sigmoid colon pseudodiverticulum formation, a complication of accidental ingestion of a toothpick that was diagnosed and successfully managed colonoscopically.
Figures

References
-
- Reddy SK, Griffith GS, Goldstein JA, Stollman NH. Toothpick impaction with localized sigmoid perforation: successful colonoscopic management. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;50:708–709. - PubMed
-
- Henderson CT, Engel J, Schlesinger P. Foreign body ingestion: review and suggested guidelines for management. Endoscopy. 1987;19:68–71. - PubMed
-
- Webb WA. Management of foreign bodies of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1988;94:204–216. - PubMed
-
- Li SF, Ender K. Toothpick injury mimicking renal colic: case report and systematic review. J Emerg Med. 2002;23:35–38. - PubMed
-
- Tenner S, Wong RC, Carr-Locke D, Davis SK, Farraye FA. Toothpick ingestion as a cause of acute and chronic duodenal inflammation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1860–1862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

