Hitting HIV where it hides
- PMID: 18241337
- PMCID: PMC2253557
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-15
Hitting HIV where it hides
Abstract
The recent finding that inhibitors of PI3/Akt can sensitize HIV infected macrophages to oxidative stress-induced cell death suggest a potential new therapeutic approach to targeting HIV reservoirs.
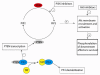
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel PI3K/Akt inhibitors screened by the cytoprotective function of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021781. Epub 2011 Jul 12. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21765914 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the PI3K/Akt cell survival pathway to induce cell death of HIV-1 infected macrophages with alkylphospholipid compounds.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 30;5(9):e13121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013121. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20927348 Free PMC article.
-
Akt inhibitors as an HIV-1 infected macrophage-specific anti-viral therapy.Retrovirology. 2008 Jan 31;5:11. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-11. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18237430 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal role of Akt activation in mitochondrial protection and cell survival by poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 inhibition in oxidative stress.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 21;280(42):35767-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507075200. Epub 2005 Aug 22. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16115861
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 eliminates HIV-1 (D3)-transduced cytoprotective human macrophages by inhibiting the AKT pathway.J Med Food. 2014 Aug;17(8):849-54. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2013.3020. Epub 2014 Jul 1. J Med Food. 2014. PMID: 24983400
Cited by
-
Bioinformatic analysis of neurotropic HIV envelope sequences identifies polymorphisms in the gp120 bridging sheet that increase macrophage-tropism through enhanced interactions with CCR5.Virology. 2015 Jul;481:210-22. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.01.032. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25797607 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-related proteins prolong macrophage survival through induction of Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 9;7:42028. doi: 10.1038/srep42028. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28181540 Free PMC article.
-
Novel HIV-1 knockdown targets identified by an enriched kinases/phosphatases shRNA library using a long-term iterative screen in Jurkat T-cells.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 17;5(2):e9276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009276. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20174665 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic expression of HIV-1 Nef impairs spatial and recognition memory.Neurobiol Dis. 2013 Jan;49:128-36. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Neurobiol Dis. 2013. PMID: 22926191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dybul M, Daucher M, Jensen MA, Hallahan CW, Chun TW, Belson M, Hidalgo B, Nickle DC, Yoder C, Metcalf JA, Davey RT, Ehler L, Kress-Rock D, Nies-Kraske E, Liu S, Mullins JI, Fauci AS. Genetic characterization of rebounding human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in plasma during multiple interruptions of highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Virol. 2003;77:3229–3237. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.5.3229-3237.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Popovic M, Tenner-Racz K, Pelser C, Stellbrink HJ, van Lunzen J, Lewis G, Kalyanaraman VS, Gallo RC, Racz P. Persistence of HIV-1 structural proteins and glycoproteins in lymph nodes of patients under highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:14807–14812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506857102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhoopat L, Rithaporn TS, Khunamornpong S, Bhoopat T, Taylor CR, Thorner PS. Cell reservoirs in lymph nodes infected with HIV-1 subtype E differ from subtype B: identification by combined in situ polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. Mod Pathol. 2006;19:255–263. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800527. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

