A cost minimisation analysis of a telepaediatric otolaryngology service
- PMID: 18241356
- PMCID: PMC2270267
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6963-8-30
A cost minimisation analysis of a telepaediatric otolaryngology service
Abstract
Background: Paediatric ENT services in regional areas can be provided through telemedicine (tele-ENT) using videoconferencing or with a conventional outpatient department ENT service (OPD-ENT) in which patients travel to see the specialist. The objective of this study was to identify the least-cost approach to providing ENT services for paediatric outpatients.
Methods: A cost-minimisation analysis was conducted comparing the annual costs of the two modes of service provided by the Royal Children's Hospital (RCH) in Brisbane. Activity records were reviewed to analyse volume of activity during a 12 month period in 2005, i.e. number of clinics, duration of clinics, number of consultations via telemedicine and in outpatient clinics, diagnoses, and travel related information. A sensitivity analysis was conducted using factors where there was some uncertainty or potential future variation.
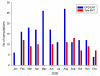
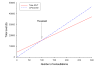
Results: During the study period, 88 ENT consultations were conducted via videoconference for 70 patients at Bundaberg Base Hospital. 177 ENT consultations were conducted at the RCH for 117 patients who had travelled from the Bundaberg region to Brisbane. The variable cost of providing the tele-ENT service was A$108 per consultation, compared with A$155 per consultation for the conventional outpatient service. Telemedicine was cheaper when the workload exceeded 100 consultations per year. If all 265 consultations were conducted as tele-ENT consultations, the cost-savings would be $7,621.
Conclusion: The cost-minimisation analysis demonstrated that under the circumstances described in this paper, the tele-ENT service was a more economical method for the health department of providing specialist ENT services.
Figures
References
-
- Queensland Health Queensland Health Annual Report 2005–2006. Brisbane Queensland Government. 2006.
-
- Harris C. Childhood ENT disorders: When to refer to specialists. Australian Family Physician. 2002;31:701-4–716. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly MJ, Quraishi MS, McShane DP. ENT and general practice: A study of paediatric ENT problems seen in general practice and recommendations for general practitioner training in ENT in Ireland. Irish Journal of Medical Science. 1995;164:209–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous