The many applications of acid urea polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to studies of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
- PMID: 18241794
- PMCID: PMC2277081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.10.006
The many applications of acid urea polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to studies of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
Abstract
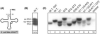
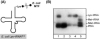
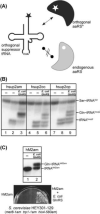
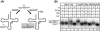
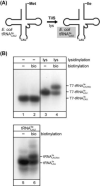
Here we describe the many applications of acid urea polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (acid urea PAGE) followed by Northern blot analysis to studies of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Acid urea PAGE allows the electrophoretic separation of different forms of a tRNA, discriminated by changes in bulk, charge, and/or conformation that are brought about by aminoacylation, formylation, or modification of a tRNA. Among the examples described are (i) analysis of the effect of mutations in the Escherichia coli initiator tRNA on its aminoacylation and formylation; (ii) evidence of orthogonality of suppressor tRNAs in mammalian cells and yeast; (iii) analysis of aminoacylation specificity of an archaeal prolyl-tRNA synthetase that can aminoacylate archaeal tRNA(Pro) with cysteine, but does not aminoacylate archaeal tRNA(Cys) with cysteine; (iv) identification and characterization of the AUA-decoding minor tRNA(Ile) in archaea; and (v) evidence that the archaeal minor tRNA(Ile) contains a modified base in the wobble position different from lysidine found in the corresponding eubacterial tRNA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery and characterization of tRNAIle lysidine synthetase (TilS).FEBS Lett. 2010 Jan 21;584(2):272-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.11.085. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 19944692 Review.
-
Structural basis for lysidine formation by ATP pyrophosphatase accompanied by a lysine-specific loop and a tRNA-recognition domain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 24;102(21):7487-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501003102. Epub 2005 May 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15894617 Free PMC article.
-
An RNA-modifying enzyme that governs both the codon and amino acid specificities of isoleucine tRNA.Mol Cell. 2003 Sep;12(3):689-98. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00346-0. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14527414
-
molecular mechanism of lysidine synthesis that determines tRNA identity and codon recognition.Mol Cell. 2005 Jul 22;19(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.007. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16039592
-
Mechanisms of the tRNA wobble cytidine modification essential for AUA codon decoding in prokaryotes.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(3):347-53. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2014.975185. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25348586 Review.
Cited by
-
Selenocysteine tRNA[Ser]Sec, the Central Component of Selenoprotein Biosynthesis: Isolation, Identification, Modification, and Sequencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1661:43-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7258-6_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 28917036 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for detecting aminoacylation and aminoacyl-tRNA editing in vitro and in cells.Isr J Chem. 2024 Sep;64(8-9):e202400009. doi: 10.1002/ijch.202400009. Epub 2024 May 6. Isr J Chem. 2024. PMID: 40066018 Free PMC article.
-
Oligodendrocyte differentiation alters tRNA modifications and codon optimality-mediated mRNA decay.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 25;13(1):5003. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32766-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36008413 Free PMC article.
-
Designer tRNAs for efficient incorporation of non-canonical amino acids by the pyrrolysine system in mammalian cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 9;46(1):1-10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1156. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29177436 Free PMC article.
-
A prophage competition element protects Salmonella from lysis.Cell Host Microbe. 2024 Dec 11;32(12):2063-2079.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.10.012. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Cell Host Microbe. 2024. PMID: 39515326
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

