Markers of inflammation before and after curative ablation of atrial flutter
- PMID: 18242542
- PMCID: PMC2247371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.10.007
Markers of inflammation before and after curative ablation of atrial flutter
Abstract
Background: Atrial arrhythmias are associated with inflammation. The cause and effect of the association are unknown.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that atrial tachyarrhythmias contribute to inflammation.
Methods: We performed a prospective observational study wherein C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels from the femoral vein and coronary sinus (CS) were compared before curative ablation for atrial flutter (AFL; n = 59) and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (SVT; n = 110). Follow-up levels were obtained at 1 and 6 months.
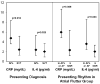
Results: Peripheral levels of both biomarkers were significantly higher in the AFL group. After multivariate adjustment, only those in the AFL group who presented in AFL or atrial fibrillation (AF) had significantly elevated CRP levels (odds ratio 1.26; P = .033). Levels of each marker were similar in the CS and peripheral blood in the SVT group; in the AFL group, both CRP and IL-6 were significantly lower in the CS than in the periphery (P = .0076 and P = .0021, respectively). CRP was significantly lower a median of 47 days after AFL ablation (from a median of 6.28 mg/L to a median of 2.92 mg/L; P = .028) and remained reduced at second follow-up. IL-6 decreased across three time points after AFL ablation (P = .002). No reduction in inflammatory biomarkers was observed after SVT ablation.
Conclusions: CRP and IL-6 levels are elevated in patients presenting in AFL. Given the lower CS values in these patients, their origin appears to be systemic rather than cardiac. Because these levels significantly fall after ablation of AFL, the atrial tachyarrhythmia appears to be the cause (not the effect) of the inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Are acute phase protein levels the link between atrial arrhythmias and inflammation?Heart Rhythm. 2008 Feb;5(2):222-3. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Heart Rhythm. 2008. PMID: 18242543 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chugh SS, Blackshear JL, Shen WK, Hammill SC, Gersh BJ. Epidemiology and natural history of atrial fibrillation: clinical implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Chung MK, Martin DO, Sprecher D, Wazni O, Kanderian A, Carnes CA, Bauer JA, Tchou PJ, Niebauer MJ, Natale A, Van Wagoner DR. C-reactive protein elevation in patients with atrial arrhythmias: inflammatory mechanisms and persistence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2001;104:2886–2891. - PubMed
-
- Fuster V, Ryden LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, Halperin JL, Le Heuzey JY, Kay GN, Lowe JE, Olsson SB, Prystowsky EN, Tamargo JL, Wann S, Smith SC, Jr, Jacobs AK, Adams CD, Anderson JL, Antman EM, Hunt SA, Nishimura R, Ornato JP, Page RL, Riegel B, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Camm AJ, Dean V, Deckers JW, Despres C, Dickstein K, Lekakis J, McGregor K, Metra M, Morais J, Osterspey A, Zamorano JL. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation--executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2001 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation) J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:854–906. - PubMed
-
- Waldo AL. The interrelationship between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. Prog Cardiovas Disease. 2005;48:41–56. - PubMed
-
- Calkins H, Leon AR, Deam AG, Kalbfleisch SJ, Langberg JJ, Morady F. Catheter ablation of atrial flutter using radiofrequency energy. Am J Cardiol. 1994;73:353–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

