Elevated blood harmane (1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) concentrations in essential tremor
- PMID: 18242711
- PMCID: PMC2291546
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2007.12.001
Elevated blood harmane (1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) concentrations in essential tremor
Abstract
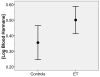
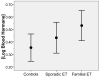
Essential tremor (ET) is a widespread late-life neurological disease. Genetic and environmental factors likely play an etiological role. Harmane (1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) is a potent tremor-producing neurotoxin. In 2002, we demonstrated elevated blood harmane concentrations in an initial sample of 100 ET cases compared to 100 controls. Between 2002 and 2007, we assembled a new and larger sample of ET cases and controls. We now attempt to replicate our previous findings. Cases and controls were frequency-matched on age, gender, and race. Blood harmane concentrations were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography. Subjects comprised 150 ET cases and 135 controls (mean age 65.3+/-15.5 vs. 65.5+/-14.2 years, p=0.94). Mean log blood harmane concentration was approximately 50% higher in cases than controls (0.50+/-0.54g(-10)/ml vs. 0.35+/-0.62g(-10)/ml, p=0.038). In a logistic regression analysis, log blood harmane concentration was associated with ET (OR(adjusted) 1.56, 95% CI 1.01-2.42, p=0.04), and odds of ET was 1.90 (95% CI 1.07-3.39, p=0.029) in the highest versus lowest log blood harmane tertile. Log blood harmane was highest in ET cases with familial ET (0.53+/-0.57g(-10)/ml), intermediate in cases with sporadic ET (0.43+/-0.45g(-10)/ml) and lowest in controls (0.35+/-0.62g(-10)/ml) (test for trend, p=0.026). Blood harmane appears to be elevated in ET. The higher concentrations in familial ET suggests that the mechanism may involve genetic factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood harmane (1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) concentration in essential tremor cases in Spain.Neurotoxicology. 2013 Jan;34:264-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Neurotoxicology. 2013. PMID: 22981972 Free PMC article.
-
Blood harmane (1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) concentrations in essential tremor: repeat observation in cases and controls in New York.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2012;75(12):673-83. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2012.688485. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2012. PMID: 22757671 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between blood harmane and harmine concentrations in familial essential tremor, sporadic essential tremor and controls.Neurotoxicology. 2010 Dec;31(6):674-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2010.08.003. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Neurotoxicology. 2010. PMID: 20708029 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-carboline alkaloids and essential tremor: exploring the environmental determinants of one of the most prevalent neurological diseases.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Sep 1;10:1783-94. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.159. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20842322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental epidemiology of essential tremor.Neuroepidemiology. 2008;31(3):139-49. doi: 10.1159/000151523. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Neuroepidemiology. 2008. PMID: 18716411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Subtle Cerebellar Features in Relatives of Essential Tremor Cases.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 17;11:605. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00605. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32765392 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating annual rate of decline: prospective, longitudinal data on arm tremor severity in two groups of essential tremor cases.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011 Jul;82(7):761-5. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2010.229740. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21436230 Free PMC article.
-
Color vision: a study of essential tremor cases versus normal controls.Eur J Neurol. 2012 Aug;19(8):1136-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2012.03688.x. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Eur J Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22417326 Free PMC article.
-
Action Tremor Asymmetry Profile Does Not Aggregate in Families with Essential Tremor.Front Neurol. 2017 Apr 19;8:148. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00148. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28469594 Free PMC article.
-
Familial aggregation of cranial tremor in familial essential tremor.Neuroepidemiology. 2013;41(1):48-53. doi: 10.1159/000348553. Epub 2013 May 25. Neuroepidemiology. 2013. PMID: 23712245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson NJ, Tyacke RJ, Husbands SM, Nutt DJ, Hudson AL, Robinson ES. In vitro and ex vivo distribution of [3H]harmane, an endogenous beta-carboline, in rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 2006;50:269–76. - PubMed
-
- Baldereschi M, Inzitari M, Vanni P, Di Carlo A, Inzitari D. Pesticide exposure might be a strong risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2007 In Press. - PubMed
-
- Benito-Leon J, Bermejo-Pareja F, Morales JM, Vega S, Molina JA. Prevalence of essential tremor in three elderly populations of central Spain. Mov Disord. 2003;18:389–94. - PubMed
-
- Benito-Leon J, Louis ED, Bermejo-Pareja F. Population-based case-control study of cognitive function in essential tremor. Neurology. 2006;66:69–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

