Rab and Arl GTPase family members cooperate in the localization of the golgin GCC185
- PMID: 18243103
- PMCID: PMC2344137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.048
Rab and Arl GTPase family members cooperate in the localization of the golgin GCC185
Abstract
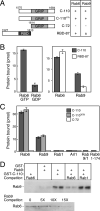
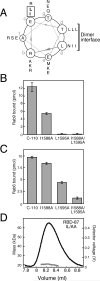
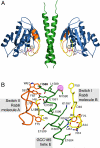
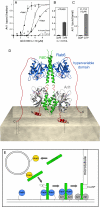
GCC185 is a large coiled-coil protein at the trans Golgi network that is required for receipt of transport vesicles inbound from late endosomes and for anchoring noncentrosomal microtubules that emanate from the Golgi. Here, we demonstrate that recruitment of GCC185 to the Golgi is mediated by two Golgi-localized small GTPases of the Rab and Arl families. GCC185 binds Rab6, and mutation of residues needed for Rab binding abolishes Golgi localization. The crystal structure of Rab6 bound to the GCC185 Rab-binding domain reveals that Rab6 recognizes a two-fold symmetric surface on a coiled coil immediately adjacent to a C-terminal GRIP domain. Unexpectedly, Rab6 binding promotes association of Arl1 with the GRIP domain. We present a structure-derived model for dual GTPase membrane attachment that highlights the potential ability of Rab GTPases to reach binding partners at a significant distance from the membrane via their unstructured and membrane-anchored, hypervariable domains.
Figures

References
-
- Barr FA. A novel Rab6-interacting domain defines a family of Golgi-targeted coiled-coil proteins. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:381–384. - PubMed
-
- Bergbrede T, Pylypenko O, Rak A, Alexandrov A. Structure of the extremely slow GTPase Rab6A in the GTP bound form at 1.8 resolution. J. Struct. Biol. 2005;152:235–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

