A randomized trial of 6-month methadone maintenance with standard or minimal counseling versus 21-day methadone detoxification
- PMID: 18243585
- PMCID: PMC2821580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.11.021
A randomized trial of 6-month methadone maintenance with standard or minimal counseling versus 21-day methadone detoxification
Abstract
Background: Important questions remain regarding the necessary duration and intensity for methadone treatment to be effective.
Methods: As part of a clinical trial of tuberculosis chemoprophylaxis [Batki, S.L., Gruber, V.A., Bradley, J.M., Bradley, M., Delucchi, K., 2002. A controlled trial of methadone treatment combined with directly observed isoniazid for tuberculosis prevention in injection drug users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 66 283-293. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(01)00208-3], patients with opioid dependence were recruited from an outpatient 21-day methadone detoxification program and were randomly assigned to one of three treatment conditions: (1) continuation in 21-day methadone detoxification; (2) transfer to 6-month methadone maintenance with only minimal counseling; or (3) transfer to 6-month methadone maintenance with standard twice monthly counseling and as-needed social work and psychiatric services. Both the 6-month maintenance treatments were followed by 1.5 months of detoxification. Urine drug tests and self-report measures were collected at baseline, months 1-6, and month 8.5.
Results: Compared to 21-day methadone detoxification, 6-month methadone maintenance with either minimal or standard counseling resulted in fewer opiate positive urine tests and days of self-reported heroin and alcohol use. There was no change in cocaine use or other outcome measures. The increased counseling available in the standard counseling condition did not appear to reduce heroin use further than the minimal counseling condition, in contrast to the effect found for more structured counseling in long-term methadone maintenance (McLellan et al., 1993).
Conclusions: Six months of methadone maintenance, even with minimal counseling, reduces heroin and alcohol use more than 21-day methadone detoxification.
Figures
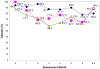
 21-day methadone detoxification,
21-day methadone detoxification,  6-month methadone maintenance with minimal counseling,
6-month methadone maintenance with minimal counseling,  6-month methadone maintenance with standard counseling.) Although the standard errors of some of the proportions may overlap [SEP = p (1-p)/n], the combined difference was statistically significant: Opiate positive urine tests months 1–6: Minimal MM vs. Detox p = .0302. Opiate positive urine tests months 1–8.5: Minimal MM vs. Detox p = .0149.
6-month methadone maintenance with standard counseling.) Although the standard errors of some of the proportions may overlap [SEP = p (1-p)/n], the combined difference was statistically significant: Opiate positive urine tests months 1–6: Minimal MM vs. Detox p = .0302. Opiate positive urine tests months 1–8.5: Minimal MM vs. Detox p = .0149.Similar articles
-
Methadone maintenance vs 180-day psychosocially enriched detoxification for treatment of opioid dependence: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2000 Mar 8;283(10):1303-10. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.10.1303. JAMA. 2000. PMID: 10714729 Clinical Trial.
-
Promoting abstinence from cocaine and heroin with a methadone dose increase and a novel contingency.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009 Apr 1;101(1-2):92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.11.006. Epub 2008 Dec 19. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009. PMID: 19101098 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized controlled trial of interim methadone maintenance.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Jan;63(1):102-9. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.1.102. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16389204 Clinical Trial.
-
[Methadone treatment and its dangers].Medicina (Kaunas). 2009;45(5):419-25. Medicina (Kaunas). 2009. PMID: 19535889 Review. Lithuanian.
-
[Abuse of alcohol and benzodiazepine during substitution therapy in heroin addicts: a review of the literature].Encephale. 2009 Jun;35(3):220-5. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19540407 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Pharmacotherapy in the treatment of addiction: methadone.J Addict Dis. 2010 Apr;29(2):200-16. doi: 10.1080/10550881003684798. J Addict Dis. 2010. PMID: 20407977 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized trial of standard methadone treatment compared to initiating methadone without counseling: 12-month findings.Addiction. 2012 May;107(5):943-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03700.x. Epub 2012 Feb 11. Addiction. 2012. PMID: 22029398 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interim treatment: Bridging delays to opioid treatment access.Prev Med. 2015 Nov;80:32-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Prev Med. 2015. PMID: 25937593 Free PMC article.
-
Methadone treatment of arrestees: A randomized clinical trial.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020 Jan 1;206:107680. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.107680. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020. PMID: 31753737 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Age related medication for addiction treatment (MAT) use for opioid use disorder among Medicaid-insured patients in New York.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2019 Jun 25;14(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13011-019-0215-4. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2019. PMID: 31238952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amato L, Davoli M, Perucci CA, Ferri M, Faggiano F, Mattick RP. An overview of systematic reviews of the effectiveness of opiate maintenance therapies: Available evidence to inform clinical practice and research. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment. 2005a;28:321–329. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2005.02.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amato L, Minozzi S, Davoli M, Vecchi S, Ferri M, Mayet S. Psychosocial combined with agonist maintenance treatments versus agonist maintenance treatments alone for treatment of opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2004;(4) doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004147.pub2. Art. No.: CD004147. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1961;4:561–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

