Design and implementation of an interactive website to support long-term maintenance of weight loss
- PMID: 18244892
- PMCID: PMC2483846
- DOI: 10.2196/jmir.931
Design and implementation of an interactive website to support long-term maintenance of weight loss
Abstract
Background: For most individuals, long-term maintenance of weight loss requires long-term, supportive intervention. Internet-based weight loss maintenance programs offer considerable potential for meeting this need. Careful design processes are required to maximize adherence and minimize attrition.
Objective: This paper describes the development, implementation and use of a Web-based intervention program designed to help those who have recently lost weight sustain their weight loss over 1 year.
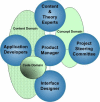
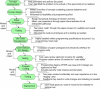
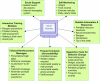
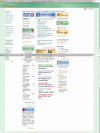
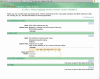
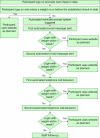
Methods: The weight loss maintenance website was developed over a 1-year period by an interdisciplinary team of public health researchers, behavior change intervention experts, applications developers, and interface designers. Key interactive features of the final site include social support, self-monitoring, written guidelines for diet and physical activity, links to appropriate websites, supportive tools for behavior change, check-in accountability, tailored reinforcement messages, and problem solving and relapse prevention training. The weight loss maintenance program included a reminder system (automated email and telephone messages) that prompted participants to return to the website if they missed their check-in date. If there was no log-in response to the email and telephone automated prompts, a staff member called the participant. We tracked the proportion of participants with at least one log-in per month, and analyzed log-ins as a result of automated prompts.
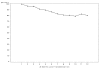
Results: The mean age of the 348 participants enrolled in an ongoing randomized trial and assigned to use the website was 56 years; 63% were female, and 38% were African American. While weight loss data will not be available until mid-2008, website use remained high during the first year with over 80% of the participants still using the website during month 12. During the first 52 weeks, participants averaged 35 weeks with at least one log-in. Email and telephone prompts appear to be very effective at helping participants sustain ongoing website use.
Conclusions: Developing interactive websites is expensive, complex, and time consuming. We found that extensive paper prototyping well in advance of programming and a versatile product manager who could work with project staff at all levels of detail were essential to keeping the development process efficient.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov NCT00054925.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Mokdad Ali H, Ford Earl S, Bowman Barbara A, Dietz William H, Vinicor Frank, Bales Virginia S, Marks James S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003 Jan 1;289(1):76–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.1.76. http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12503980jbr20304 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ogden Cynthia L, Carroll Margaret D, Curtin Lester R, McDowell Margaret A, Tabak Carolyn J, Flegal Katherine M. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999-2004. JAMA. 2006 Apr 5;295(13):1549–55. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.13.1549. http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16595758295/13/1549 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blanck HM, Dietz WH, Galuska DA, et al. State-specific prevalence of obesity among adults - United States 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2006;55:985–988. - PubMed
-
- Seidell J C, Visscher T L, Hoogeveen R T. Overweight and obesity in the mortality rate data: current evidence and research issues. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999 Nov;31(11 Suppl):S597–601. - PubMed

