Catalytic-site mutations in the MYST family histone Acetyltransferase Esa1
- PMID: 18245364
- PMCID: PMC2278108
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.080135
Catalytic-site mutations in the MYST family histone Acetyltransferase Esa1
Abstract
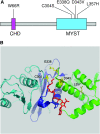
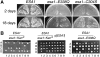
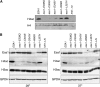
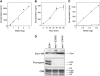
Esa1 is the only essential histone acetyltransferase (HAT) in budding yeast. It is the catalytic subunit of at least two multiprotein complexes, NuA4 and Piccolo NuA4 (picNuA4), and its essential function is believed to be its catalytic HAT activity. To examine the role of Esa1 in DNA damage repair, we isolated viable esa1 mutants with a range of hypersensitivities to the toposide camptothecin. Here we show that the sensitivity of these mutants to a variety of stresses is inversely proportional to their level of histone H4 acetylation, demonstrating the importance of Esa1 catalytic activity for resistance to genotoxic stress. Surprisingly, individual mutations in two residues directly involved in catalysis were not lethal even though the mutant enzymes appear catalytically inactive both in vivo and in vitro. However, the double-point mutant is lethal, demonstrating that the essential function of Esa1 relies on residues within the catalytic pocket but not catalysis. We propose that the essential function of Esa1 may be to bind acetyl-CoA or lysine substrates and positively regulate the activities of NuA4 and Piccolo NuA4.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Piccolo NuA4-catalyzed acetylation of nucleosomal histones: critical roles of an Esa1 Tudor/chromo barrel loop and an Epl1 enhancer of polycomb A (EPcA) basic region.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):159-69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01131-12. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23109429 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast enhancer of polycomb defines global Esa1-dependent acetylation of chromatin.Genes Dev. 2003 Jun 1;17(11):1415-28. doi: 10.1101/gad.1056603. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12782659 Free PMC article.
-
Site specificity analysis of Piccolo NuA4-mediated acetylation for different histone complexes.Biochem J. 2015 Dec 1;472(2):239-48. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150654. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26420880 Free PMC article.
-
MYST opportunities for growth control: yeast genes illuminate human cancer gene functions.Oncogene. 2007 Aug 13;26(37):5373-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210606. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17694079 Review.
-
Reading chromatin: insights from yeast into YEATS domain structure and function.Epigenetics. 2010 Oct 1;5(7):573-7. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.7.12856. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20657183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression analysis of esa1 mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae links NAB3 to transcriptional silencing and nucleolar functions.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Oct;2(10):1223-32. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.003558. Epub 2012 Oct 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 23050233 Free PMC article.
-
Gcn5 and Esa1 function as histone crotonyltransferases to regulate crotonylation-dependent transcription.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 27;294(52):20122-20134. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010302. Epub 2019 Nov 7. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31699900 Free PMC article.
-
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae model and screen to define the functional consequences of oncogenic histone missense mutations.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Jul 6;12(7):jkac120. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac120. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35567477 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetyltransferase Sas3 contributes to fungal development, cell wall integrity, and virulence in Aspergillus fumigatus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Apr 17;90(4):e0188523. doi: 10.1128/aem.01885-23. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38451077 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin and transcription in yeast.Genetics. 2012 Feb;190(2):351-87. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.132266. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22345607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amberg, D., D. Burke and J. Strathern, 2005. Methods in Yeast Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

